In this article
What is Polarizing Filter?
If you've ever taken a photo on a bright day only to find shiny spots on water, distracting reflections on glass, or skies that look pale instead of blue, you're not alone. These are common challenges for photographers and videographers. A polarizing filter helps fix them by controlling how light enters your camera lens, giving your shots more clarity and depth.
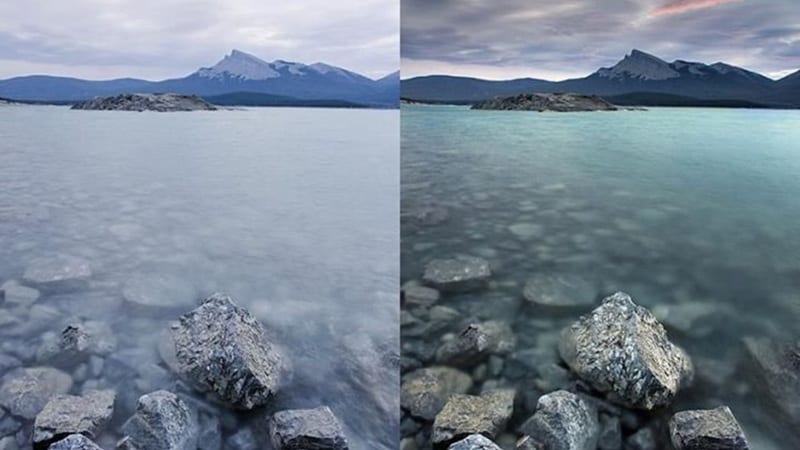

A polarizing filter is a camera lens accessory that reduces unwanted reflections, eliminates glare, and enhances colors by filtering polarized light. In videography, it's also used to create more vivid outdoor scenes, making skies richer, water clearer, and colors more balanced without heavy post-production editing.
Benefits of Using Polarizing Filters
Using a polarizing filter can transform ordinary shots into striking images by removing visual distractions and enhancing colors directly during the shot. It's a simple tool that makes a big difference in your photos and videos.
- Reduce reflections: Minimizes shiny spots on glass, water, or polished surfaces so you can see what's behind them.
- Reduce glare: Reduce the dazzling brightness caused by sunlight bouncing off reflective areas, making your images easier to view and more balanced.
- Improves Sky and Color Contrast: Turns pale skies into deep, vibrant blues and makes clouds stand out, while also improving the separation between different colors.
- Increases Saturation Naturally: Highlighting the richness in greens, blues, and other colors in landscapes without relying heavily on post-production adjustments.
The Problem with Polarizing Filters
While polarizing filters can dramatically improve your shots, they aren't without their drawbacks. Understanding these limitations will help you decide when these filters are worth using and when they might hold you back.
- Cuts Exposure by 2–3 Stops: Because the filter blocks certain light waves, less light reaches the sensor, which can make low-light shooting more difficult without adjusting ISO or shutter speed.
- Costly: High-quality polarizing filters can be expensive, especially for larger lenses or professional-grade glass.
- Angle-Dependent: The effect is strongest when shooting at about 90° to the sun, meaning results can vary depending on your position and time of day.
- Slower Setup: You need to rotate the filter to achieve the desired effect, which can slow you down in fast-paced shooting situations.
- Hard to Preview: In some conditions, it's tricky to judge the final look through the viewfinder or screen until after the shot is taken.
- Needs Maintenance: Fingerprints, dust, and smudges can reduce its effectiveness, so regular cleaning is essential.
How a Polarizing Filter Works
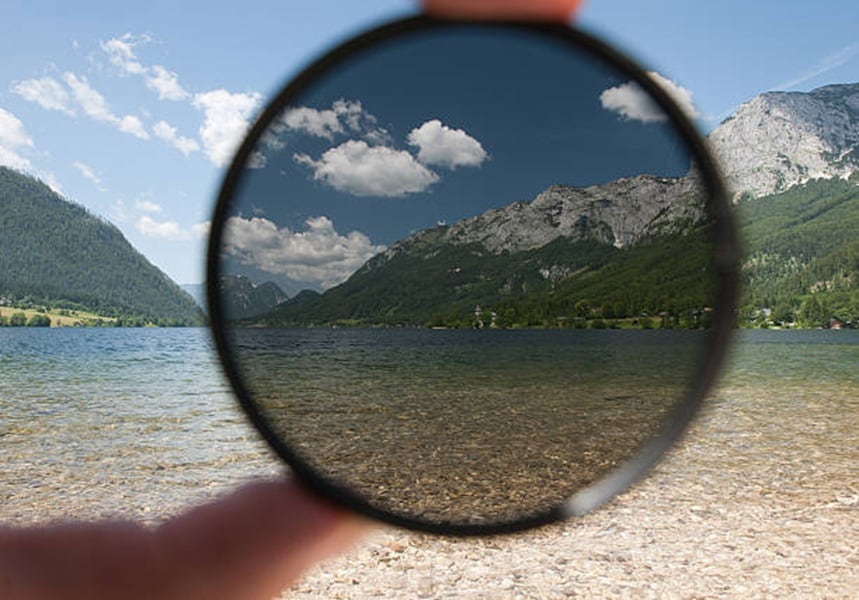
Polarizing filters work by allowing only light waves moving in a specific direction to pass through while blocking the rest. This is similar to window blinds, where adjusting the slats controls how much light enters and reduces unwanted glare.
When sunlight reflects off surfaces like water, glass, or shiny leaves, the light waves become organized in one direction, which creates glare and dulls colors. By rotating a polarizing filter, you can align it to block these specific light waves, removing glare and revealing the natural colors underneath.
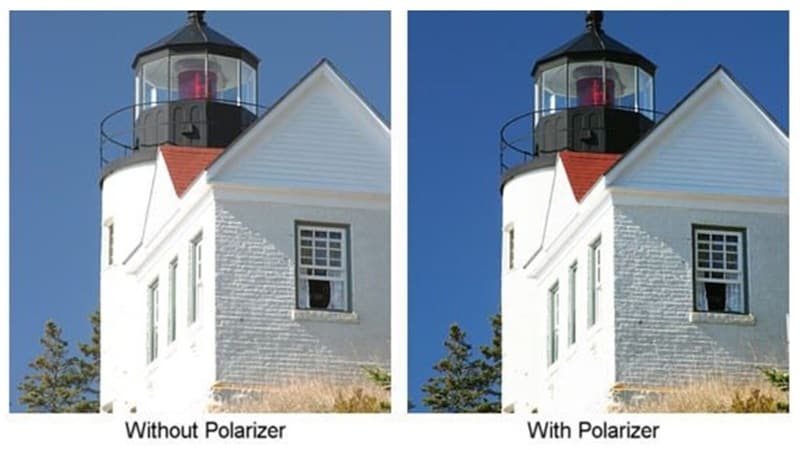

Most modern versions are circular polarizers (CPLs), which combine a polarizing layer with an optical element that ensures your camera's autofocus and light metering still function properly. This way, you get glare reduction and richer colors without affecting camera performance.
Types of Polarizing Filters
Polarizing filters are available in two main types: linear and circular. The terms do not describe the filter's shape but rather how each type alters the light that passes through it. Knowing the difference will help you choose the right filter for your camera and shooting style.
- Linear Polarizing Filter
- Circular Polarizing Filter (CPL)
A linear polarizer blocks light waves that are not aligned with its filtering pattern, effectively eliminating glare and reflections. It works well for film cameras or simple optical systems. However, on modern digital cameras, linear polarizing filters can sometimes interfere with autofocus and through-the-lens (TTL) light metering.
A circular polarizer starts with the same process as a linear polarizer, then adds an extra optical element called a quarter-wave plate. This transforms the filtered light into a form that does not disrupt autofocus or TTL metering systems. CPLs are the most common choice for DSLR and mirrorless cameras.
Linear vs. Circular Polarizing Filters
|
Feature |
Linear |
Circular |
|
How It Works |
Filters light waves in one direction to reduce glare and reflections |
Use linear polarization first, then a quarter-wave plate to make it compatible with camera sensors |
|
Compatibility |
Best with older film cameras or fully manual systems |
Compatible with modern DSLR cameras and mirrorless cameras without affecting autofocus or light metering functions |
|
Price |
Usually more affordable |
Typically more expensive due to additional optical elements |
|
Autofocus/TTL Metering |
It may interfere with autofocus and TTL light metering functions on modern cameras |
Fully compatible with autofocus and TTL light metering |
|
Use Case |
Controlled shooting environments, manual focus photography |
General photography and videography, especially when speed and automation are important |
How Much Does a Polarizing Filter Cost?
If you plan to buy a polarizing filter, the price can vary significantly depending on the size, quality, and brand.
Entry-level filters generally cost from around $20 to $60 and are suitable for casual photography or beginners who want to try the effect without spending too much. Mid-range options usually cost between $60 and $175, offering better glass quality, multi-coating, and more durable construction. Professional-grade filters, which often use premium materials and advanced coatings, can cost $200 or more.
Typical Price Ranges:
|
Price Range |
What to expect |
|
20–60 USD |
Basic circular polarizers from well-known brands, suitable for everyday use |
|
60–175 USD |
Higher optical quality, better coatings, and improved durability |
|
200 USD and above |
Professional filters with premium glass, weather sealing, and exceptional color accuracy |
Application Section - When/Where to Use Polarizing Filter
A polarizing filter is a versatile tool for photography and filmmaking. This filter helps control reflections, deepen colors, and manage contrast, making it especially valuable in scenes where light and reflections can be distracting. From capturing serene landscapes, shooting through glass, to creating a stylish cinematic look, polarizing filters let creators shape light for the exact mood they want.
Common Applications and Examples in Popular Media




Common Mistakes When Using Polarizing Filters
Not every scene benefits from a polarizer. Overuse can cause uneven exposure or unwanted darkening, so attach it only when needed.
Not every scene benefits from a polarizer. Overuse can cause uneven exposure or unwanted darkening, especially in low-light conditions or when shooting wide-angle landscapes.
Attach the filter only when needed for specific effects like reducing reflections or enhancing sky contrast. Remove it when shooting in low light or when the effect isn't necessary.
The polarizing effect is strongest when shooting at a 90-degree angle to the sun. Ignoring this can result in inconsistent or weak effects across your images.
Position yourself so your shooting direction is perpendicular to the sun's direction for maximum effect. Use a compass app if needed to find the optimal angle.
Polarizing filters reduce the amount of light entering the lens by 2-3 stops, which can lead to underexposed images if not compensated for.
Adjust your exposure settings (ISO, aperture, or shutter speed) to compensate for the light loss when using a polarizing filter.
Practical Demonstration Section - How to Use a Polarizing Filter
A polarizing filter can make skies appear richer, colors pop, and glare vanish. Here's a simple guide to help you use it effectively.

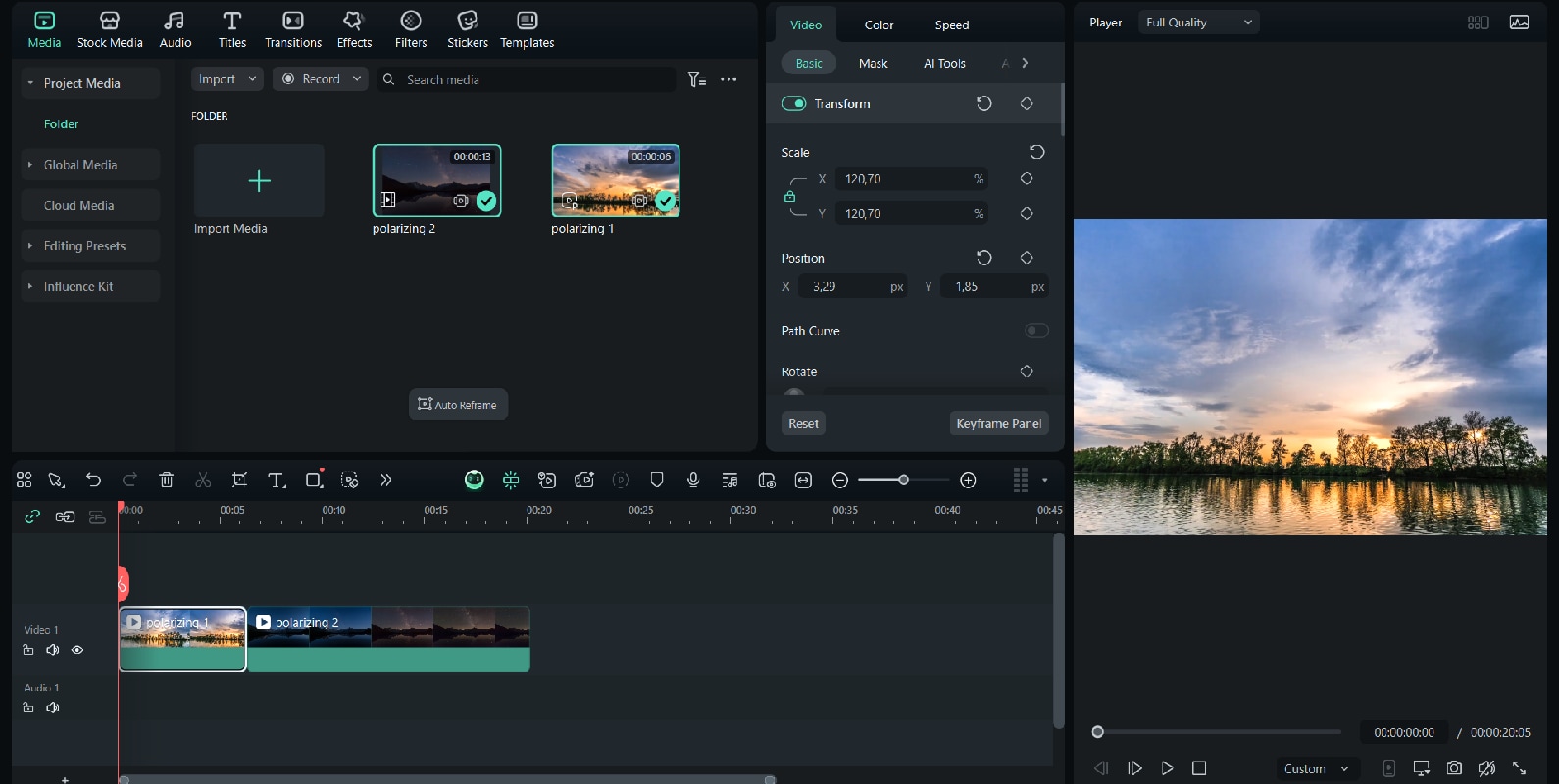
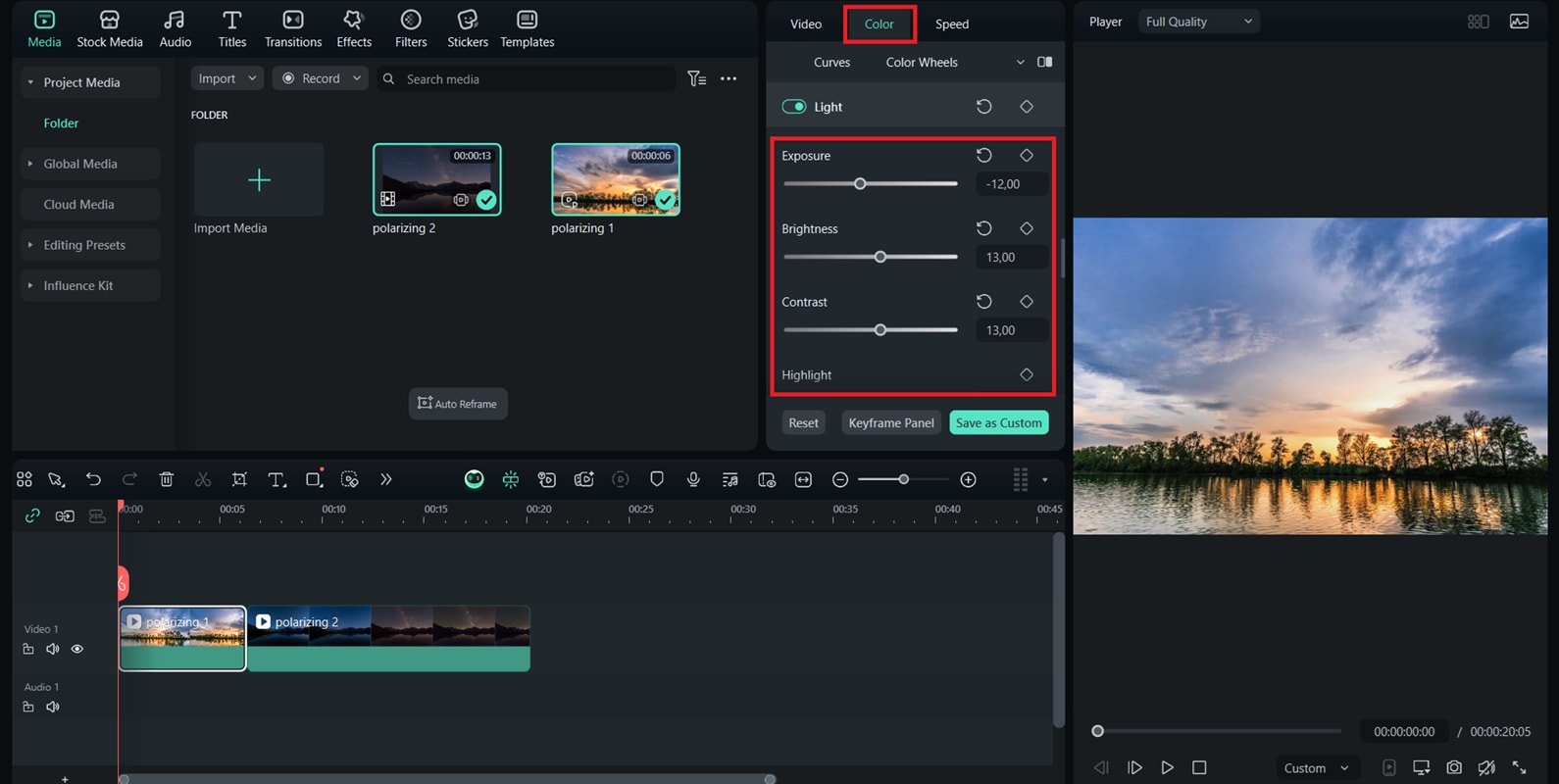
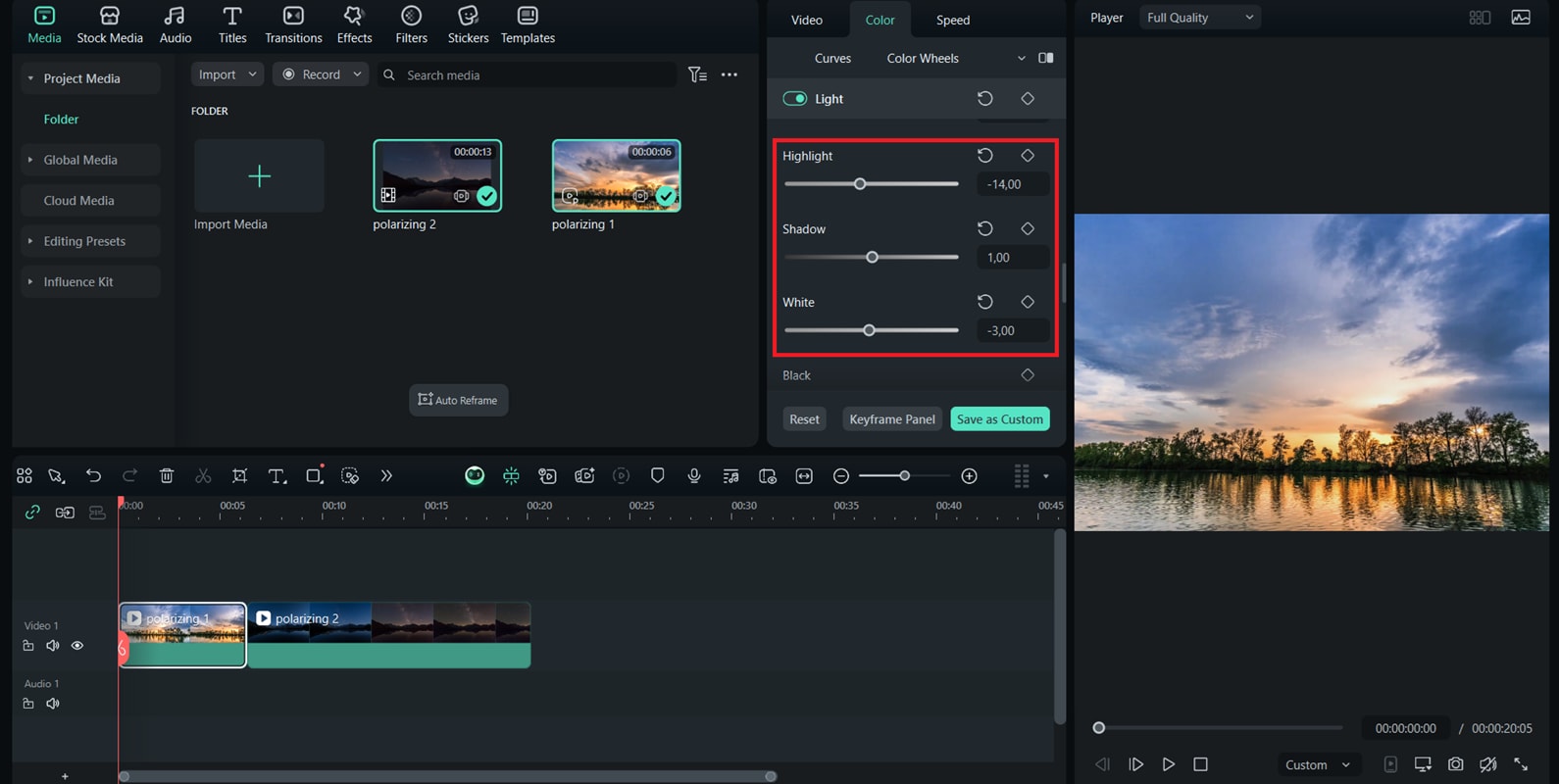
How to Apply Filters in Post-production
While a polarizing filter can bring impressive results during shooting, you can also recreate a similar effect in post-production. Using editing tools, you can reduce glare, enhance colors, and give your footage a polished, cinematic look without needing extra gear.





