In this article
Understanding 32-bit Audio
If you're working with video, you've probably encountered audio that clips, distorts, or just doesn't sound clean. In this guide, you'll learn about what 32-bit audio is and how it changes the way sound gets recorded and handled.
32-bit float audio is a high-resolution format that captures sound with exceptional clarity and range.
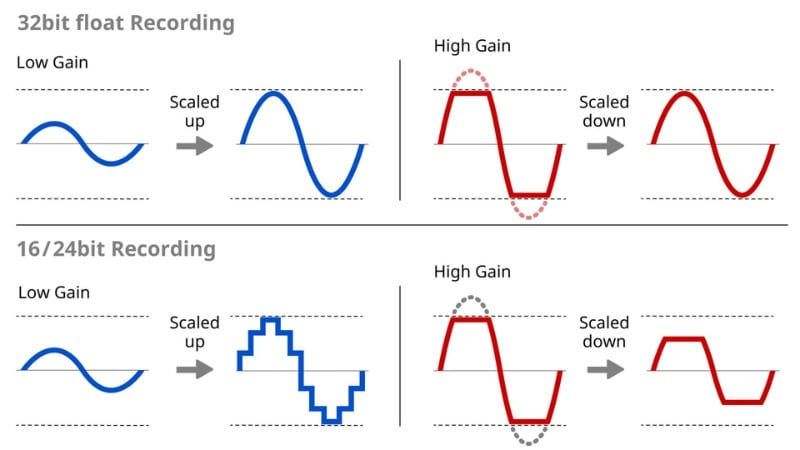
Unlike 16-bit or 24-bit audio, it uses floating-point numbers to record audio data without fixed limits or distortion. With 32-bit floating point audio, you can record both whispers and loud peaks in the same take. There's no need to worry about distortion or constantly adjusting gain levels.
What is Bit Depth?
Bit depth refers to how much audio detail gets recorded. It's like how resolution works for images. The higher the bit depth, the more detail and volume range it can capture.
When comparing 32-bit float vs 24-bit, the difference lies in flexibility and safety during recording. Let's break it down:
| Feature | 32-bit | 24-bit | 16-bit |
| Dynamic Range | ~1520 dB | 144 dB | 96 dB |
| Clipping Protection | Immune to clipping | Can clip if too loud | Easily clips |
| File Size | Large | Medium | Small |
| Editing Flexibility | Extremely high | Moderate | Limited |
Benefits of 32-bit Audio
The Importance of 32-bit Audio in Video Production
- 32-bit float audio can keep dialogue clean without the need for retakes.
- You'll get professional-quality sound without constantly adjusting levels.
- No ruined takes due to mic level mistakes, giving you less pressure and more freedom while shooting.
- Because the audio file has more flexibility, editors can recover or enhance details without distortion.
When We Should Use 32-bit Audio
After learning what 32-bit float audio is, let's discuss when you should use it. The truth is, you don't always need it. Let's break down the scenarios where 32-bit audio really shines.

Common Applications



Common Challenges of 32-Bit Audio
How to Use 32-bit Audio
So, you've learned what 32-bit float audio is and when to use it. Now let's talk about how it actually works, and how to use it in your video editing workflow.

32-bit audio uses floating-point math instead of fixed values to capture sound. This gives it a much larger dynamic range and makes it nearly impossible to clip. Even if your input levels are too high or too low, the audio remains clean and can be adjusted later without losing quality.
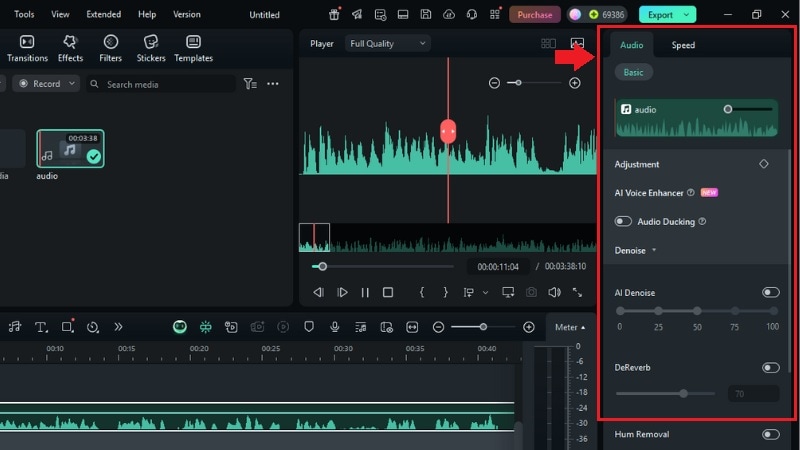
Editing 32-Bit Audio with Filmora
If you're editing video and want to work with 32-bit float audio, it's important to use software that supports it. One option is Wondershare Filmora, which supports high-resolution audio formats and allows you to clean, balance, and fine-tune your audio.
Here are some of the audio editing features in Filmora:
- Auto Beat Sync – Match external audio to your video clips.
- Audio Ducking – Automatically reduce background music during voice or dialogue.
- AI Audio Denoise – Clean up unwanted sound, such as wind, echoes, or keyboard clicks.
- Keyframe Volume Control – Adjust audio levels across your timeline.
- AI Audio Enhancer – Improve clarity for vocals and dialogue in your video.
Pro Tip: Since Filmora is also a powerful video editor, you don't have to juggle between different apps. You can edit your 32-bit audio and video together in one workspace.
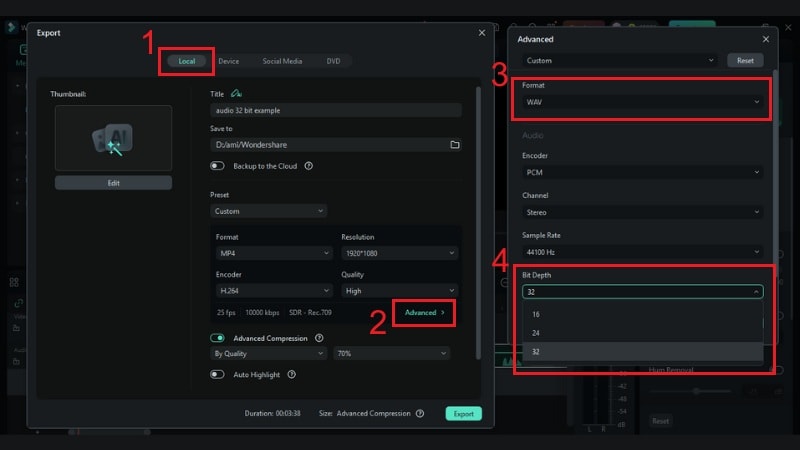
How to Use and Edit 32-bit Float Audio in Filmora
Here's a quick 3-step guide for editing 32-bit float audio inside Filmora: