In this article
Definition Section - What is Color Space
Almost every pro camera today lets you pick from different color spaces, but a lot of creators still aren't sure what they mean or how to pick the right one. At its core, color space is a way of defining the range of colors that can be captured and reproduced. To understand this concept better, let's break down the definition of color space in more detail.
Color space is a mapped spectrum of colors represented by numerical values. In a video, it determines the specific, measurable range of colors and brightness levels available for your footage. The main role of color space is to outline how natural, vivid, or cinematic your video will look once it's graded and displayed. Since different devices may use different color spaces, choosing the right one is essential to keep your footage consistent across devices.
Why Color Spaces are Important
- Consistent Colors Across Devices: Color spaces make sure your footage looks the same no matter where you view it. Without them, the colors might shift from one screen to another, either too dark or oversaturated.
- Better Editing Control: When you edit, the color space sets the boundaries of what you can adjust. Working in a wider color space gives you more room to push contrast, saturation, and tones without breaking the image, so you can color grade more freely.
- Accurate Color Reproduction: Getting natural skin tones or the perfect shade of blue in the sky depends on accurate color reproduction. The right color space makes sure your footage stays true to reality instead of looking dull or oversaturated.
- Platform Compatibility: Different platforms expect different color spaces. Matching your project to the right standard keeps your video looking the way it should when it goes live.
- Support for HDR and 4K Content: The right color space ensures HDR and 4K video look sharper with richer colors. You can take full advantage of today's displays and make your clip pop with cinematic vibrancy.
Two Categories of Color Spaces
Color spaces can generally be divided into two main categories: device-independent and device-dependent.
- Device-dependent color spaces: A device-dependent color space defines color based on the limitations of a specific device. For example, a monitor, printer, or camera can only reproduce a certain subset of colors, and its color space reflects that range. In other words, they give you a picture of that device's unique "color limits."
- Device-independent color spaces: A device-independent color space describes color in absolute, universal terms rather than tying it to one device. They usually operate behind the scenes and aren't something most creators adjust directly during editing.
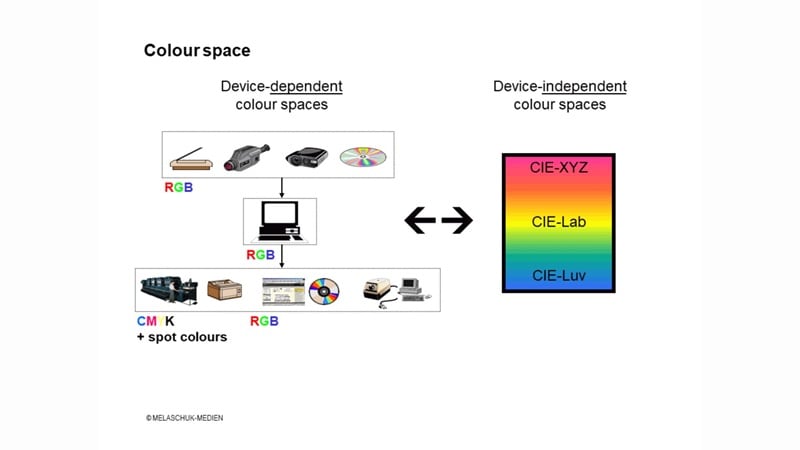
Image: Melaschuk Medien
Essential Concepts in Color Space
When learning about what a color space is in video, you may come across a few key terms that shape how color is captured, processed, and displayed. These concepts form the foundation for understanding why color space matters in video editing and playback.
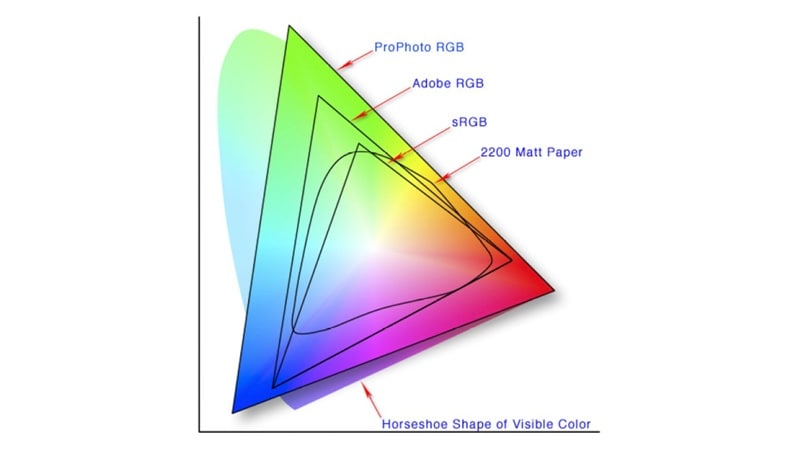
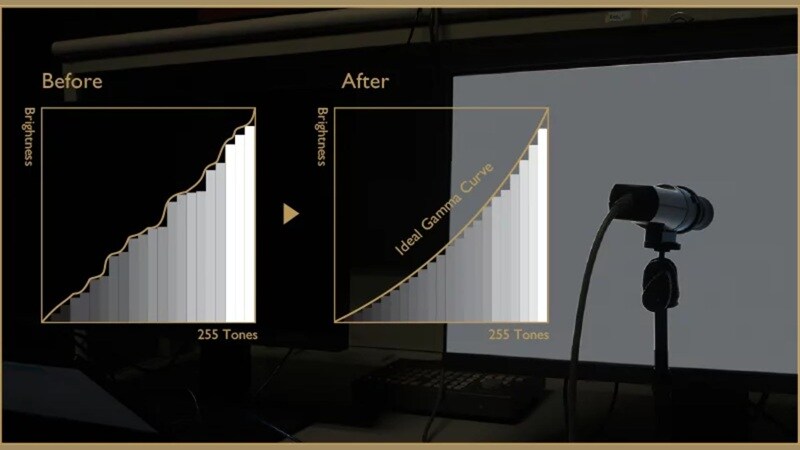
Application Section - When/Where to Use Color Space
How Color Space Is Used in Video Production:
By now, you can see that color space influences your video at every stage of production:
Stage 1. Filming: The moment you hit record, the selected color space defines the range of colors and brightness your camera can store.
Stage 2. Editing and Grading: During post-production, color space controls how much flexibility you have when adjusting tones, balancing colors, or adding a creative style with colors. It's the foundation that determines how far you can push your grade without losing quality.
Stage 3. Export and Share: At the final stage, color space ensures your video looks correct on its target platform. Choosing the right one helps your video appear consistent across YouTube, television, cinema, or HDR screens.
Common Applications:




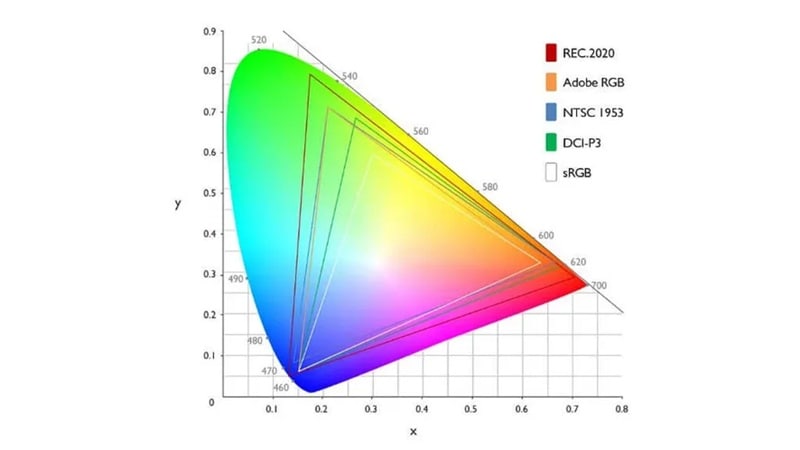
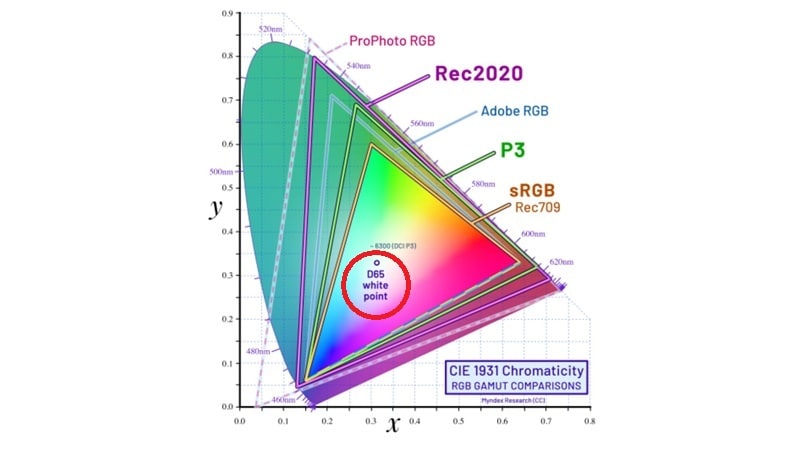
Common Types of Color Spaces and Their Uses
We've briefly mentioned a few color spaces and their applications, but the table below provides a clearer breakdown of the most common ones and how they're used.
|
Color Space |
Use Case |
|
sRGB |
Web, monitors, digital cameras, online video |
|
Adobe RGB |
Print, professional photography |
|
Rec. 709 (ITU-R BT.709) |
HD video, broadcast, streaming platforms |
|
Rec. 2020 (ITU-R BT.2020) |
4K/8K UHD, HDR video production and display |
|
DCI-P3 |
Digital cinema projection, high-end displays |
|
P3-D65 |
Wide-gamut displays (common in Apple devices), streaming platforms, HDR mastering |
|
HDR - Rec.2100HLG |
High Dynamic Range video using Hybrid Log Gamma, live broadcast HDR |
|
HDR - Rec.2100HLG |
High Dynamic Range video using Perceptual Quantizer, HDR10, Dolby Vision mastering |
|
Rec. 601 (ITU-R BT.601) |
Legacy SD video (NTSC, PAL, SECAM) |
|
ACES |
Film, TV, VR production, long-term archiving |
|
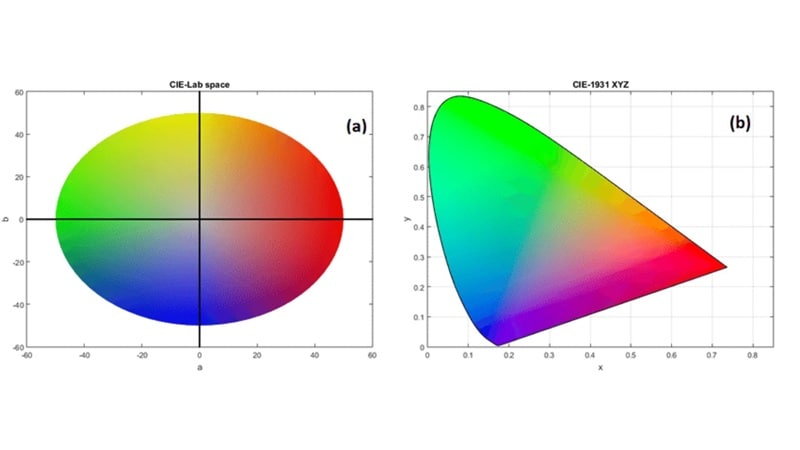
CIE 1931 RGB / XYZ |
Reference standard, scientific comparison |
|
CIE Lab |
Image editing, printing, perceptual corrections |
|
YCbCr (Y′CbCr / YPbPr) |
Video compression, broadcast, streaming |
Key Principles and Best Practices of Color Space
- Color Spaces Are Interchangeable, But Not Perfectly
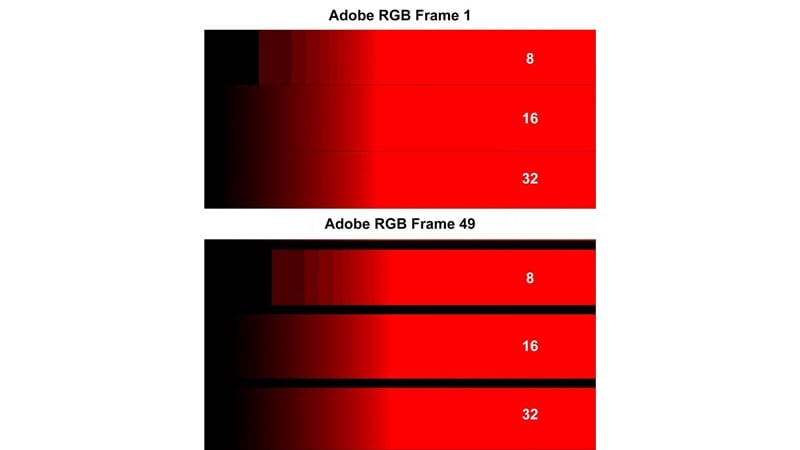
Any color space can be converted into another with the right math. However, some challenges may come if you move from a larger gamut into a smaller one. Some colors can fall outside the target range and cannot be reproduced, which are known as out-of-gamut values. You can map or clip them in different ways, but some loss of color information is unavoidable.
- Every Project Requires at Least One Color Space Conversion
No matter how simple your project is, at some point you will need a conversion. Most of the time, it is just moving from your camera's color space to the one used for your final video. Since cameras and delivery formats rarely match, this step is almost guaranteed. Knowing how it works keeps you from being surprised later in the edit.
- Grading Tools React Differently in Different Spaces
Color wheels, curves, and sliders do not behave the same way in every space. The math behind them changes with the color space you are working in. That is why many editors prefer to use a large "intermediate" space for grading. It makes your tools more predictable and gives you better results.
- Shrink Color Space Gradually from Capture to Delivery
The best practice is to capture in a wide color space, preserve as much information as possible during editing, and only reduce the gamut when exporting for the target display. Once colors are clipped outside a delivery space, they are gone permanently.
Common Challenges in Color Spaces
Working with color spaces is not always smooth. Even if you follow best practices, a few common challenges can easily affect how your final video looks.
Repeated encoding can degrade color accuracy, causing banding or washed-out tones.
Use high-quality, intermediate codecs like ProRes or DNxHR during editing. Save heavy compression for final delivery only, and avoid multiple re-encodes of the same file.
Ambient lighting and screen glare can distort perceived color space.
Grade in a neutral-lit environment and check your work on multiple calibrated displays to see how it will appear.
Not all screens are built the same. A video graded in Rec. 2020 might look great on an HDR display, but look flat on an older monitor that only supports sRGB.
Export in a color space that matches your target audience's display (check the table above for guidance) and provide alternate versions if possible.
Even if you did well on the grading, wrong color space or gamma settings can distort colors during playback.
Double-checking your export presets before rendering will save you from problems later. Run a short test export to confirm everything looks correct.
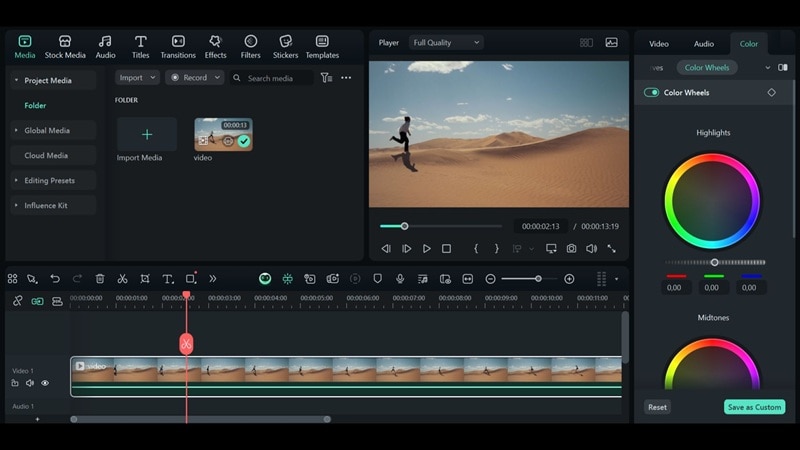
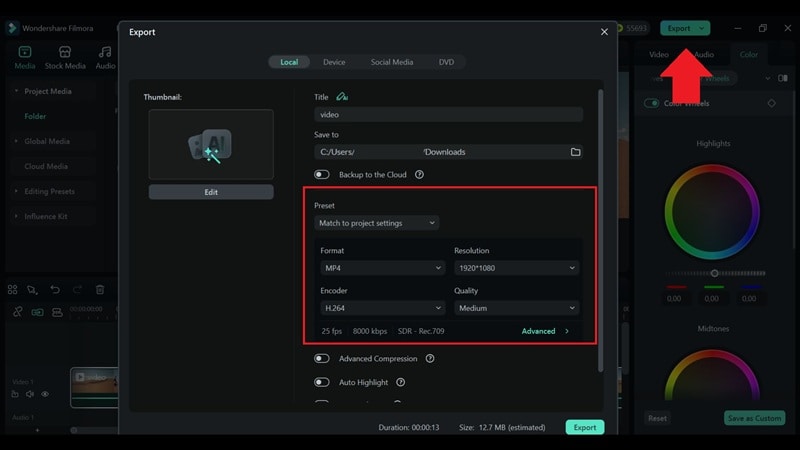
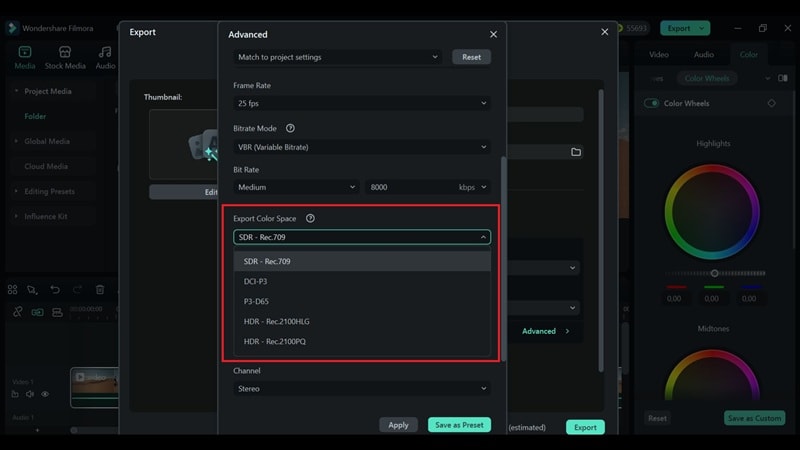
Practical Demonstration Section - How to Use
Given the importance of color space, we will cover how to set it up and export using an easy video editor like Wondershare Filmora. Filmora supports standard formats like Rec. 709, DCI-P3, and more, along with built-in color grading tools to help you correct, balance, and stylize your footage.
How to Set Color Space and Export in Filmora