In this article
Understanding Video Encode
If you have experienced slow video upload or download, the unrest and frustration is always on another level. You watch the loading bar like it owes you money. You close the app and reopen it, still stuck. At this point, encoding the video might be the best solution. But then, what does it mean to encode a video?
The term "video encode" refers to the process of turning large video files into smaller, shareable versions without ruining the quality. Think of it like folding a huge blanket into a small drawer. Nothing's lost, just packed smarter. In this guide, you will learn about video encoders and how they work.

The term "What is video encode?" means turning raw video data into a compressed, small digital format. A video encoder reads the raw file and then restructures it using algorithms. These algorithms remove duplicate data and compress visuals to ensure they work across devices. Compression during this operation helps to compress the data, reducing the file size.
You can compress a file without changing its format. But video encode always transforms the structure. So while encoding includes compression, not all compression counts as encoding.
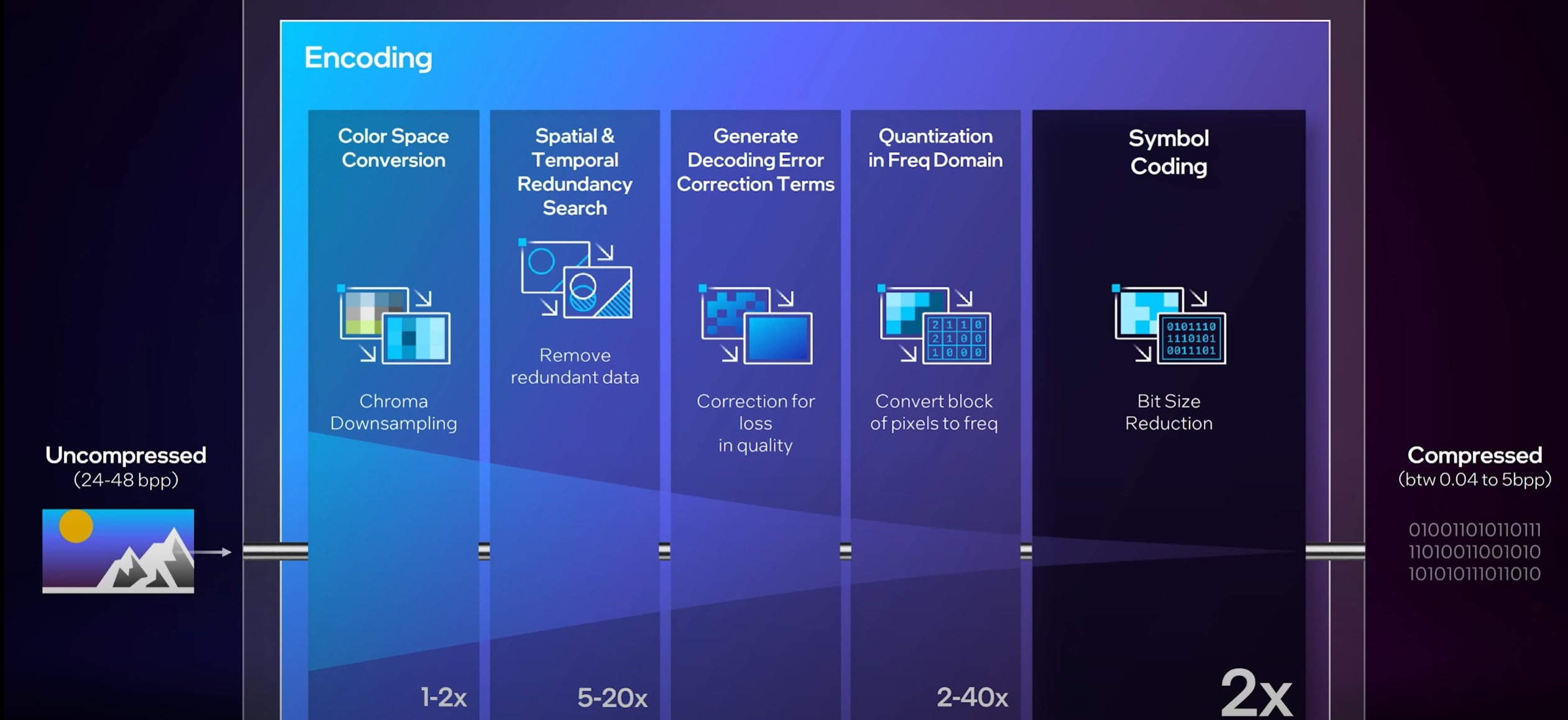
Why is Video Encoding Needed?
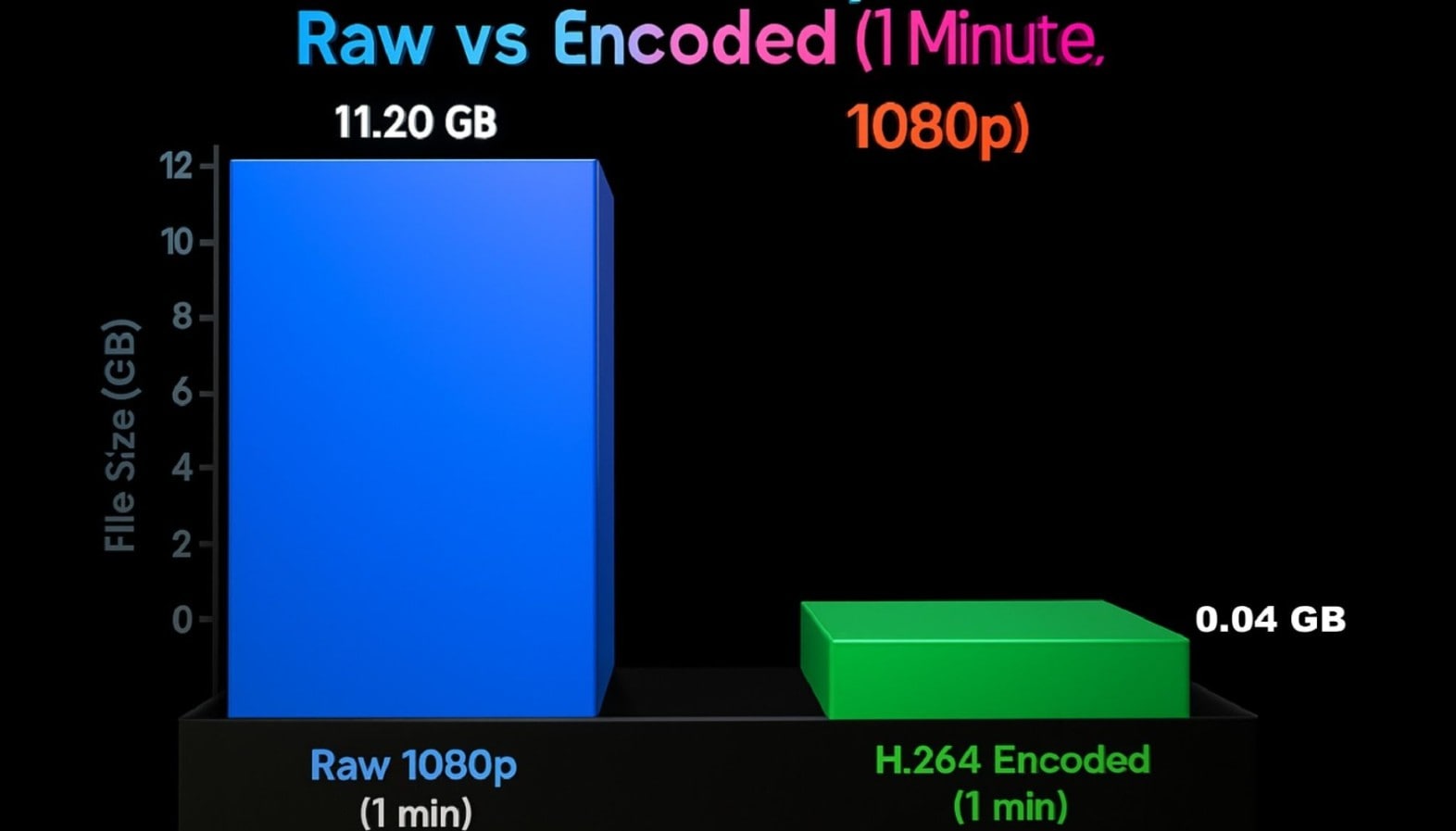
Recent tests in 2025 by Meta showed that smart encode workflows cut video file sizes by 60 percent without visible loss, which is of major importance. A typical example is shown in a 1-minute 1080p raw video, which is around 11.2 GB. After encoding with H.264, it shrinks to just 0.0375 GB (about 37.5 MB) while maintaining good visual quality.
Below are other top reasons why video encoding is a great introduction.
Encoding vs. Transcoding
Remember, we stated that Video encoding is the process of turning raw video data into a shareable format. Think of it as turning flour into bread.
Transcoding is when you take an already-encoded file and convert it again, maybe to a smaller size, a different codec, or a new resolution. This ensures compatibility with older devices and unstable networks. That's more like slicing the bread to fit your toaster.
Compression plays a role in both, but it's not the same. Video compression is just one tool inside encoding or transcoding. It's like the oven heat. You adjust it depending on what you're baking.
| Feature | Encoding | Transcoding |
| Input | Raw video (uncompressed) | Encoded video file |
| Purpose | Convert raw to viewable | Change format or specs |
| Compression | Applied during conversion | Often re-applied or adjusted |
| When Used | First export from the camera or software | For re-uploads, streaming, or cross-platform delivery |
| Output | New compressed video | Reformatted video for new use |
Key Elements of Video Encode
So, what happens under the hood when you use a video encoder? Behind that smooth export button, there's a whole line of moving parts.
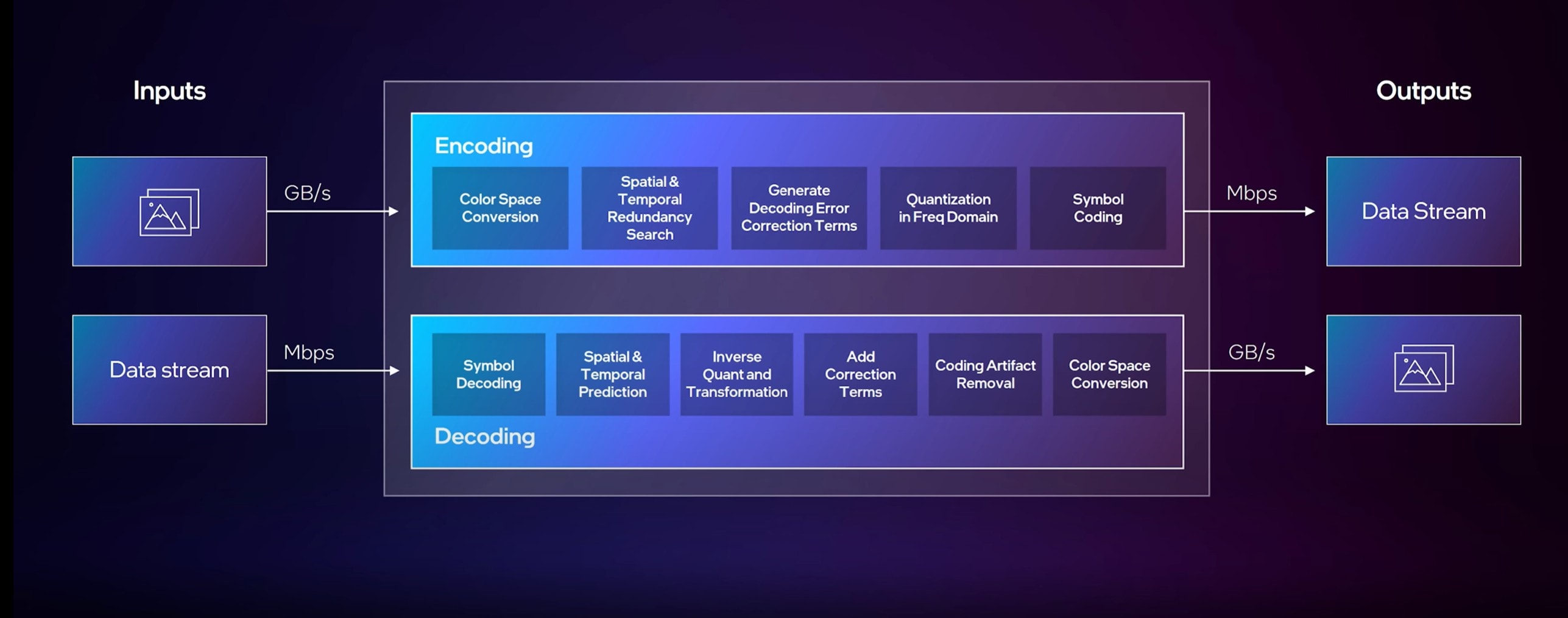
Together, they shape how the video encode process delivers size, speed, and quality. Here's a quick breakdown of these elements.
- Preprocessing: Cleans the raw footage. Removes noise, adjusts color, or resizes the frame.
- Video Compression: Reduces data size by removing redundancy. Keeps video quality close to the original.
- Intra-frame Compression (I-frames): Compresses one frame at a time. Great for high-detail scenes and random access.
- Inter-frame Compression (P/B-frames): Uses data from surrounding frames to save space. Best for smooth playback.
- Transform (DCT, etc.): Converts pixel data into frequency data using tools like the DCT transform. Saves more space.
- Quantization: Rounds frequency values for smaller file sizes. It may slightly reduce visual detail.
- Entropy Coding (CABAC/Huffman): Encodes repeated data efficiently. Think of it like smart storage labels.
- Bitrate Control (CBR, VBR, CRF): Manages how much data is used per second. Balances quality with file size.
- Packaging/Container Format: Bundles your video, audio, and subtitles into one file. Examples include MP4, MKV, or MOV.
Elements of Video Encoding Priority Tabulated
| Element | Always used in any encoding workflow | Purpose (Uses based on specific goals) |
| Preprocessing | ✅ | Prepares raw footage (color, de‑interlacing) |
| Intra-frame Compression | ✅ | Critical for editing and GOP key‑frame accuracy |
| Inter-frame Compression | ✅ | Used in streaming and storage to reduce bitrate |
| Transform (e.g., DCT) | ✅ | Converts spatial data into the frequency domain |
| Quantization | ✅ | Balances quality vs. file size |
| Entropy Coding | ✅ | Packs quantized data into efficient bit streams |
| Bitrate Control | ✅ | Ensures target quality and transmission constraints |
| Packaging/Container | ✅ | Required for final delivery (MP4, MKV, HLS) |
| Chroma Subsampling | Optional | Useful for streaming and mobile delivery |
| GOP Structure | Optional | Impact seeking, ABR, and coding efficiency |
| Macroblocks / CTUs | Optional | Better compression in H.264/HEVC/AV1 |
| Multi-pass Encoding | Optional | Important for high-quality master files |
| Adaptive Bitrate Streaming | Optional | Key for platforms like Netflix & YouTube |
| Hardware vs. Software Encoding | - | Choose based on live vs post-production scenarios |
Popular Format and Codecs Used in Video Encoding
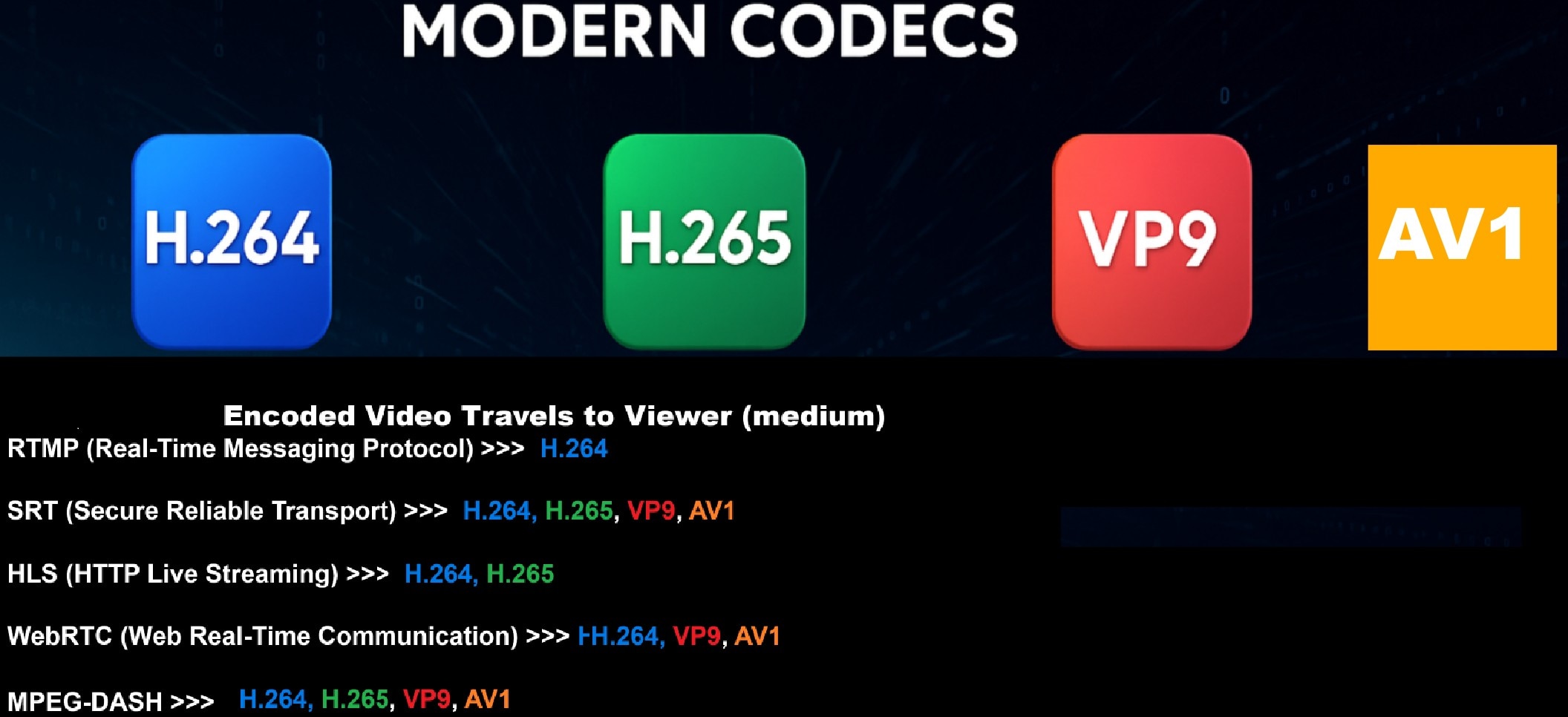
When you export your video, you usually pick a format or codec. A video encoder needs the right codec to balance size, speed, and quality. Let's break down the most-used codecs in 2025.
| Feature | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) | AV1 | VP9 |
| Compression Efficiency | Medium | High | Very High | High |
| Best For | Quick exports, older devices | UHD content, storage saving | Streaming at scale | Web playback |
| Video Quality @ Same Bitrate | Good | Better | Excellent | Good |
| File Size | Larger | Smaller | Smallest | Small |
| Hardware Support | Excellent | Moderate | Growing in 2025 | Good |
| Software/Browser Support | Universal | Mixed | Expanding | Strong |
| Encoding Speed | Fast | Slower | Slowest | Moderate |
| Use Cases | Editing, Sharing | 4K, OTT content | Streaming platforms | Browser-based video |
Factors that Affect Video Encoding
Factors that affect video encoding include:
How Video Encoding Powers Today's Video Workflows
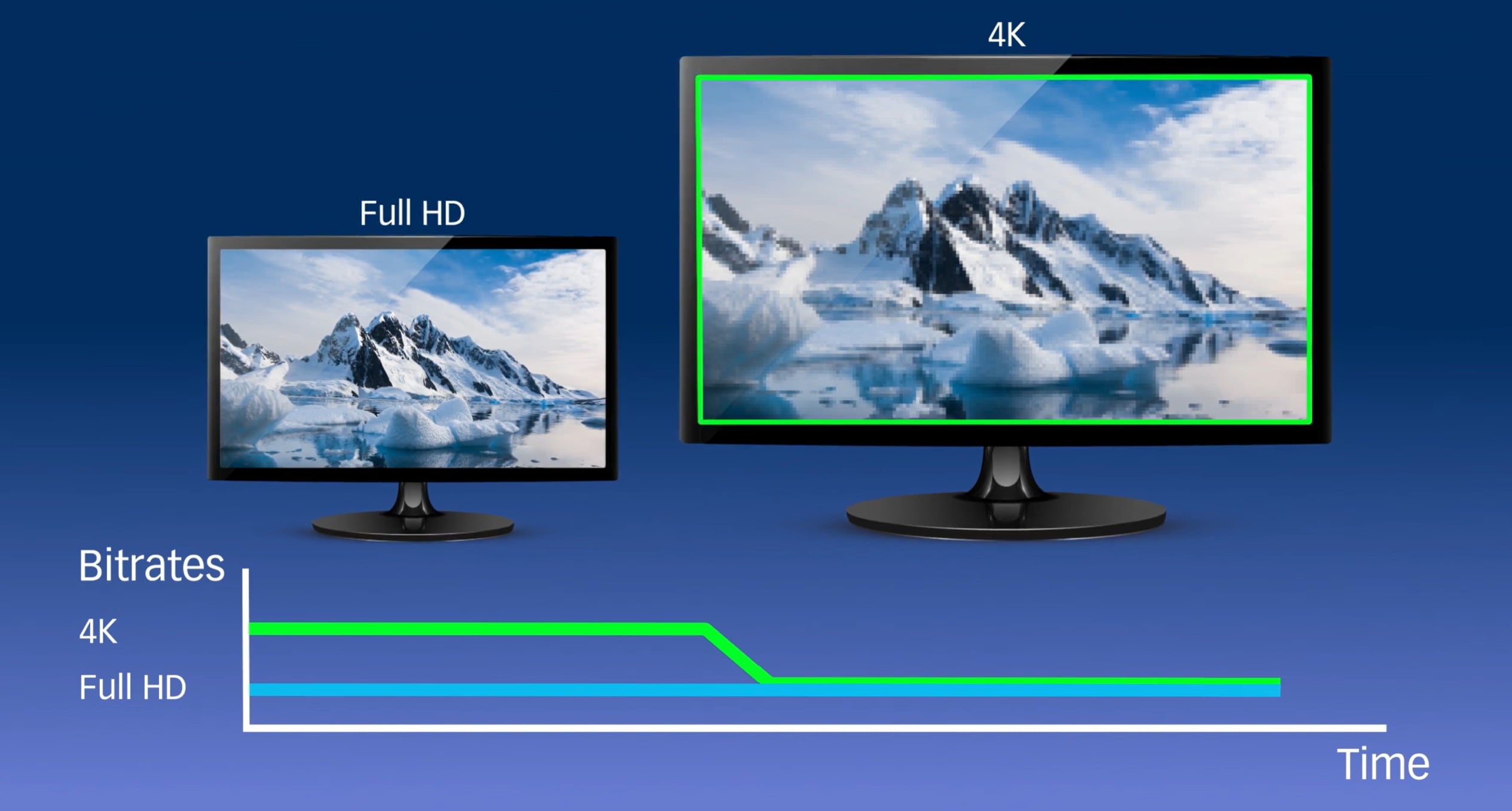

You shoot and edit, and then you must adapt that footage for various platforms. Without video encode, your videos wouldn't flow smoothly through production pipelines. A top encoder ties all workflow pieces together, and this is based on some key concepts.
Different Applications of Video Encoding
Video Encoding Pitfalls Every Creator Should Know
Once you encode a video with flawed steps, the result will suffer. These mistakes are common. Avoid them early.
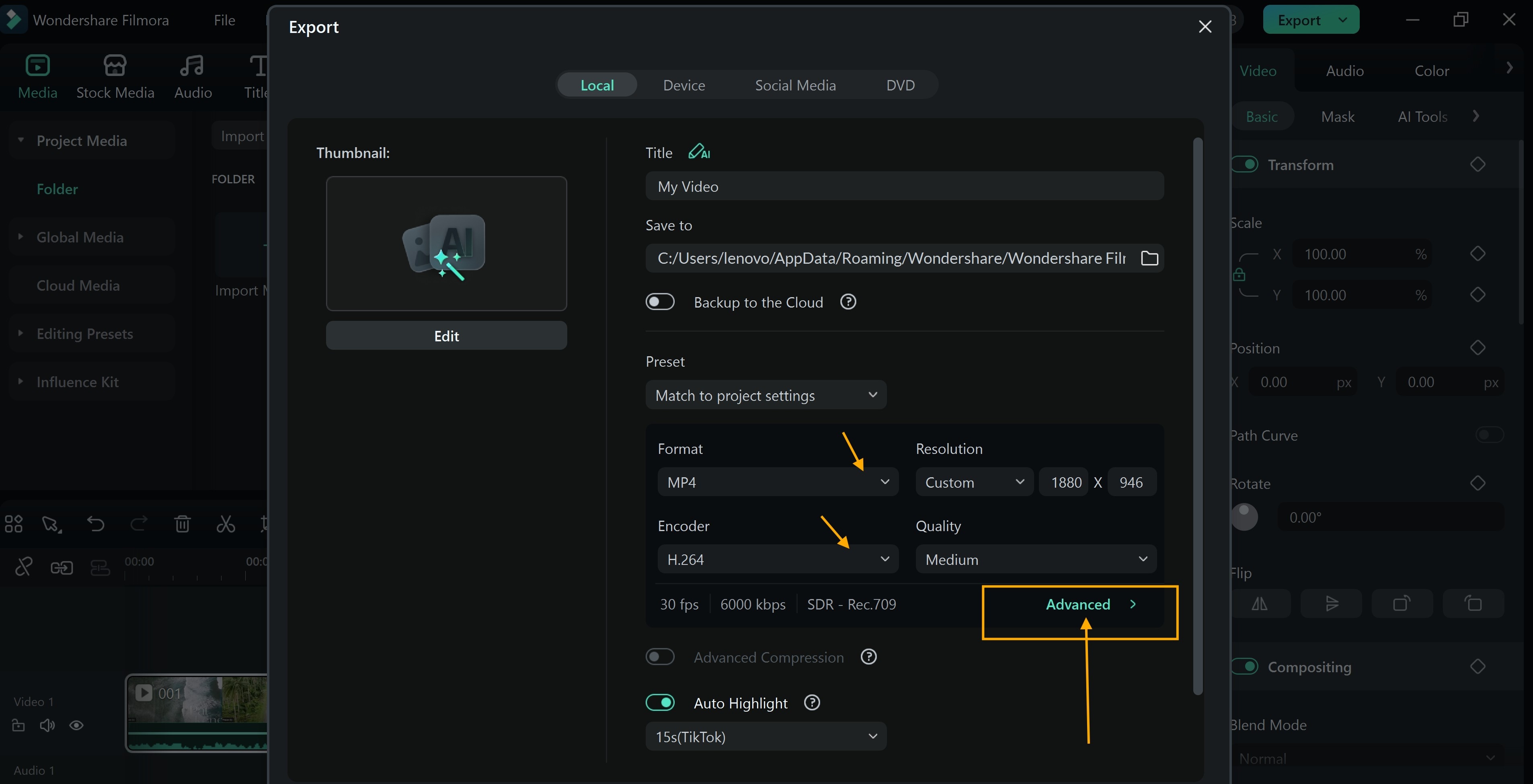
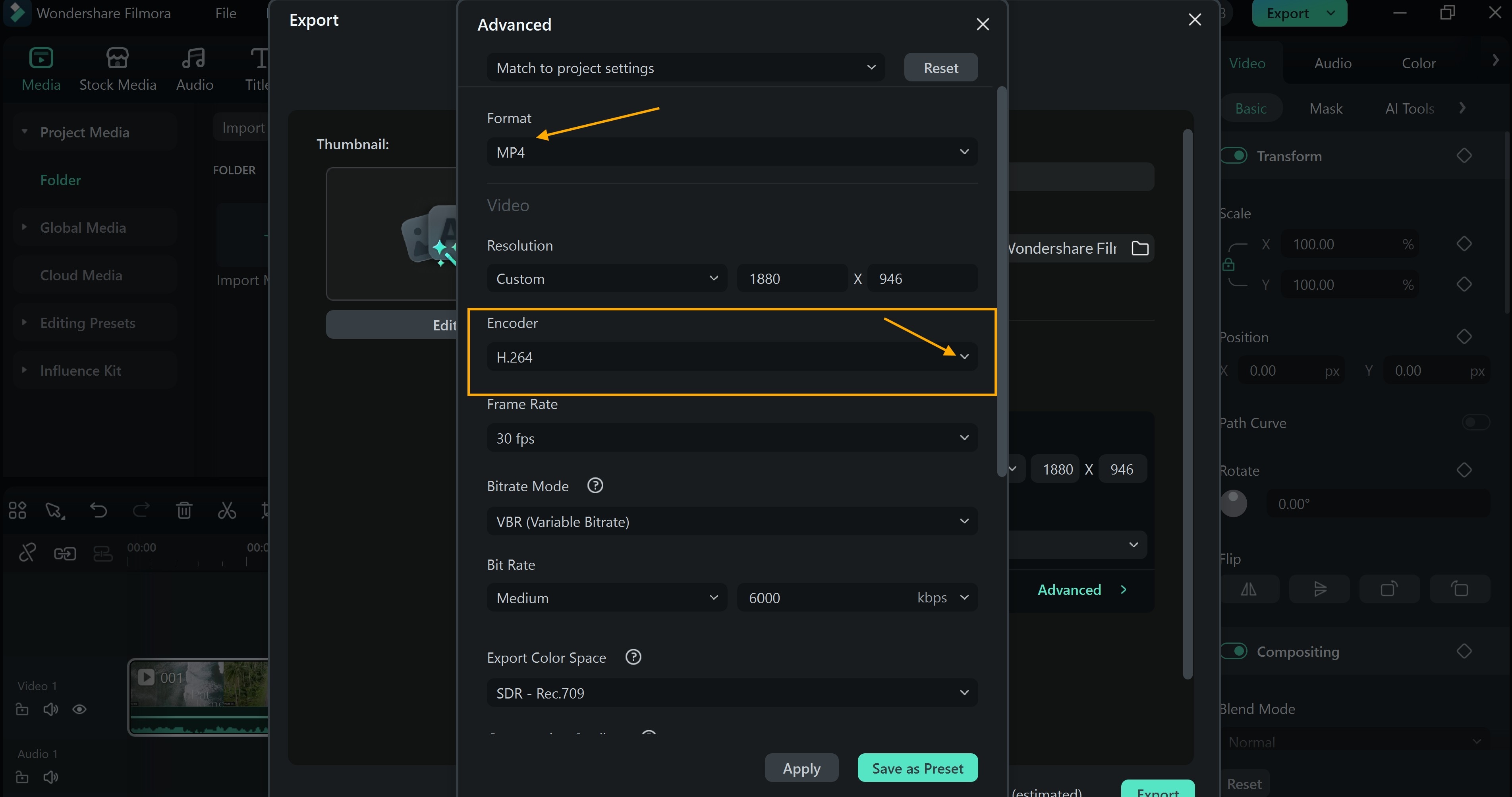
Encoding Videos Automatically With Filmora

Wondershare Filmora simplifies video encoding with automatic tools built for creators. You don't need expert knowledge to use its smart video encoder. Below is how to encode videos with Filmora.
Pro Tips for Video Encoding in Filmora
Bonus: General Video Encoding Best Practices
Advancement in the Field of Video Encoding

Conclusion
You've seen how video encode transforms raw footage into viewable files. A smart video encoder ensures that it happens smoothly, efficiently, and accurately. Choosing the right video encoding path matters, and Filmora is a top option.
With built-in encoding presets, custom export settings, and real-time previews, Filmora simplifies the entire process, making it easy for creators of all levels to turn raw clips into shareable videos without stress.





