Video compression solves a problem that many of us face. Ever tried to share a video only to find it too large to send through messaging apps or email? You might be eager to share videos with friends and family only to find out that there is a file size limitation. This is often the case with many social media applications.
As such, video compression comes into play. However, this is also where the question “What is video compression?” arises. If you have the same question, you’re lucky. In this article, you’ll go through this technology that makes it possible to share, stream, and store videos efficiently in this digital world.
In this article
Part 1. What Is Video Compression?
Video compression is a process that reduces the size of a video file. However, it often comes with the drawback of reduced video quality. It’s about making videos smaller by removing redundant or less critical data from the original file.
Why Is Video Compression Necessary?
This technology is necessary for several reasons. First, it allows for efficient storage of video content. High-quality videos would quickly fill up hard drives and cloud storage without compression. Second, it enables smoother streaming experiences. Compressed videos require less bandwidth, making it possible to watch online content without constant buffering.

Difference Between Compressed and Uncompressed Videos
Uncompressed videos, in a nutshell, contain all the original data captured by a camera or recording device. They retain the same quality that a video recorder can offer. For better cameras, this comes with bigger file sizes. For instance, a minute of raw 4K video could easily exceed several gigabytes.
Compressed videos, as already discussed, offer smaller file sizes. While this can result in some quality loss, sending them through different apps is easier. Thankfully, technology has evolved to make compressed videos retain their quality.
Part 2. The Science Behind Video Compression
Video compression employs various techniques to reduce file size while preserving as much visual quality as possible. To learn what a compressed video is, you should know these concepts.
Spatial Compression
Spatial or intraframe compression focuses on reducing redundancy within individual video frames. This method is similar to how image compression works. It identifies areas of similar color or patterns within a frame and represents them more efficiently.
For example, spatial compression might use a single code to represent that entire area instead of storing information for each pixel in a large blue sky. This technique is particularly effective for scenes with large, uniform areas or repetitive patterns.
Temporal Compression
Temporal compression, or inter-frame compression, takes advantage of similarities between consecutive frames in a video. Most videos contain scenes where much of the image remains unchanged from one frame to the next. Temporal compression identifies these static elements and only stores the differences or changes between frames.

For instance, in a video of a person talking against a static background, only the movements of the speaker’s face and mouth must be encoded for many frames, significantly reducing the data needed.
One of the best video compression tool for all kinds of scenarios.
Filmora allows you to choose the video compression by quality or by Youtube uploading requirements.
Key Technical Terms in Video Compression
To fully grasp what is a compressed video, it’s essential to understand several key technical terms:
- Codec (Coder-Decoder). A codec is a software or hardware that compresses and decompresses digital video. It implements a specific algorithm or set of rules for compression. Popular video codecs include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and VP9. The codec choice can significantly impact the compressed video’s file size and quality.
- Bitrate. Bitrate refers to the amount of data processed per unit of time, typically measured in bits per second (bps). A higher bitrate generally means better video quality but larger file sizes. Video compressors often allow users to set a target bitrate, balancing quality against file size based on their needs.
- Resolution. This is the number of pixels in each video frame, usually expressed as width x height (e.g., 1920x1080 for Full HD). Higher resolutions contain more detail but require more data. Video compression can involve reducing the resolution to decrease file size, a process known as downscaling.
These elements work together in the compression process. For example, a codec might use both spatial and temporal compression techniques, adjusting its approach based on the content of the video. The bitrate determines how much data the codec can use to represent the video, influencing the balance between quality and file size. Resolution affects the amount of detail the codec needs to process and store.
Part 3. Types of Video Compression and Formats
Video compression comes in different forms, each with advantages and use cases. This section will explore the types and formats of video compression. This will further your understanding of what a compressed video is.
Types of Video Compression
There are two primary types of video compression: lossless and lossy.
😄Lossless Compression
Lossless compression reduces file size without losing any original data. When decompressed, the video is identical to the original without quality loss. This method is perfect for scenarios where every detail matters, like professional video editing or medical imaging. However, it only slightly reduces file size.
😥Lossy Compression
Lossy compression greatly reduces file size by permanently removing some data. It discards less noticeable information, leading to some quality loss. Modern lossy compression algorithms are advanced, maintaining high visual quality while significantly shrinking the file size.

Comparison Between the Two Compression Types
Comparing the two:
- Lossless compression offers perfect quality but limited file size reduction.
- Lossy compression provides substantial file size reduction but at the cost of some quality loss.
- Due to its efficiency, lossy compression is more commonly used for everyday video applications.
Common Video Compression Formats
Now, here are the common video compression formats used today:
- H.264/AVC (Advanced Video Coding): H.264 is widely used for recording, compressing, and distributing video. It offers good compression efficiency and is supported by most devices and platforms. This format is commonly used for streaming services, Blu-ray discs, and broadcasting.
- H.265/HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding): H.265 is the successor to H.264 and provides better compression efficiency. It can deliver the same visual quality as H.264 at about half the bitrate, making it ideal for 4K and 8K video content. However, it needs more processing power for encoding and decoding.
- VP9: Developed by Google, VP9 is an open, royalty-free video coding format designed to compete with H.265 in compression efficiency. It’s widely used on YouTube and supported by many web browsers, making it popular for web-based video content.
- AVI (Audio Video Interleave): AVI is an older container format developed by Microsoft. Although it’s not a compression method itself, AVI files can contain video compressed with various codecs. It’s less efficient than modern formats but is still used because of its compatibility with different software and systems.
Each of these formats has its strengths and is suited for different scenarios. H.264 remains a popular all-rounder, H.265 and VP9 are ideal for high-resolution content and efficient streaming, while AVI is sometimes used for its broad compatibility.
Part 4.Game-Changing Tool for Video Compression: Wondershare Filmora
Now that you’ve learned all about Video Compression, it’s time to try it out. Wondershare Filmora is a powerful video editing tool that also excels in video compression, making it a valuable asset for anyone looking to reduce file sizes without compromising quality.
Whether you’re working with large video files or need to meet specific platform requirements, Filmora offers a range of features to help you compress videos efficiently. To be specific, here are the key features of Filmora:
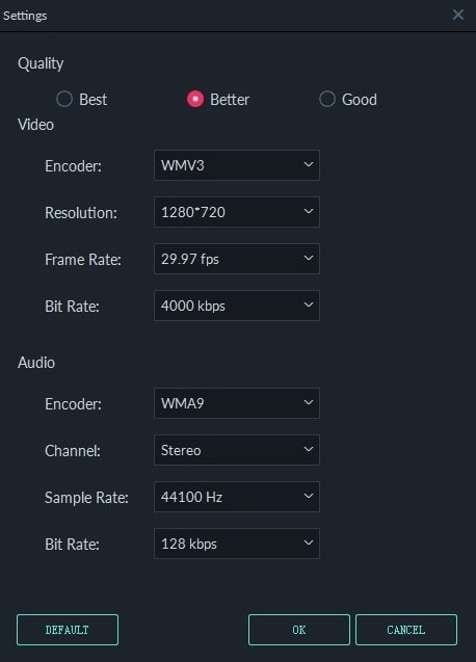
- Customizable export settings. Wondershare Filmora provides you with many export settings, such as bit rate, resolution, and formatting. This means that your final outputs will fit any purpose you want them to.
- Built-in compression presets. Filmora also offers compression formats for popular video-hosting platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, TikTok, etc.
- Custom resolution and frame rate settings. Paired with the Auto Compression feature, Wondershare Filmora lets you control your export resolution and frame rate settings.
How To Compress Videos With Wondershare Filmora
To begin learning what video compression is and how to do it with Filmora, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Install, download, and launch Wondershare Filmora. Sign up or log in with a Wondershare, Facebook, Google, X (formerly Twitter), or Apple account.
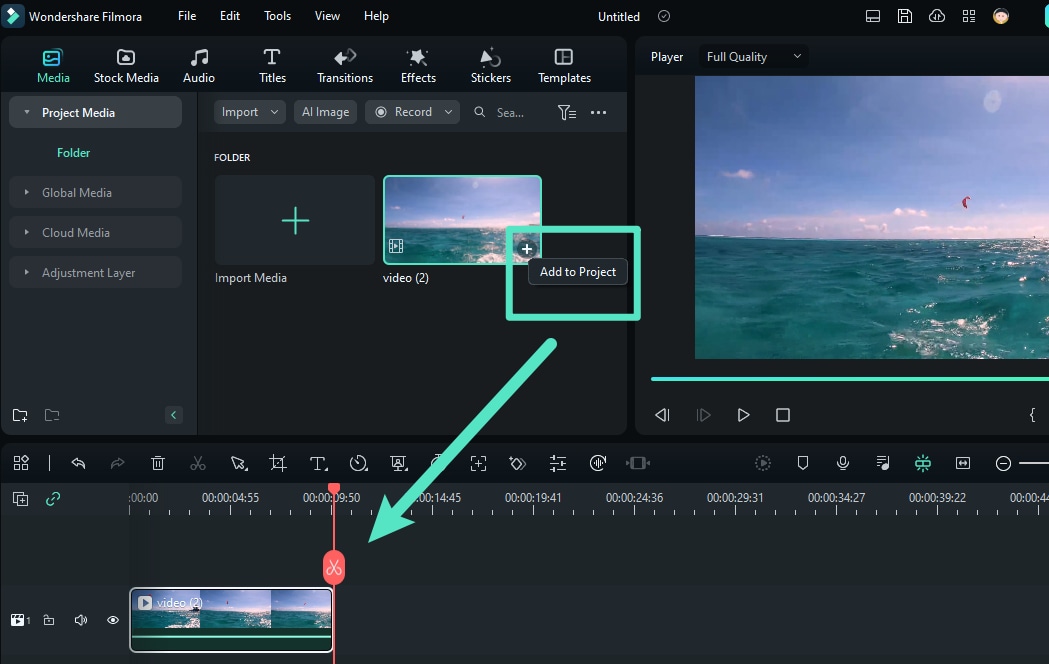
Step 2: Click +New Project on the homepage. Then, Import your MOV file.
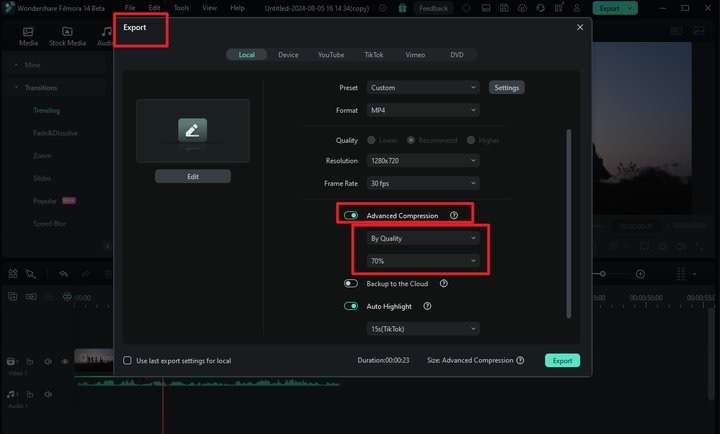
Step 3: Go to the Export window. Then, toggle Advanced Compression. Afterward, set it to By Quality and adjust the compression rate below it. Once done, click Export.
Conclusion
In this article, you’ve learned what a compressed video is. You’ve also read about techy terms like spatial and temporal compression techniques. You’ve also examined popular compression formats such as H.264, H.265, and VP9.
For those looking to compress videos easily while maintaining quality, Filmora is an excellent choice. Its Auto Compression feature simplifies the process and offers a comprehensive video editing and manipulation tool suite. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned creator, Filmora provides an efficient solution for your video compression needs.




 100% Security Verified | No Subscription Required | No Malware
100% Security Verified | No Subscription Required | No Malware
