
Did you ever upload a photo on social media to find it strangely truncated or distorted? Or maybe watched a movie with black bars on each side of the screen. These issues often arise from aspect ratio, which is the proportionate relationship between the width and height of an image. Understanding what does aspect ratio means regarding creating and displaying visual content is important.
This guide deeply dives into aspect ratios, unpacking their meaning and application across different media formats. From photos and videos to movies and social media platforms, you will learn valuable lessons on choosing the best aspect ratio for each platform so that your content looks fabulous.
In this article
Part 1: The ABCs of Aspect Ratio: Understanding Width and Height
Aspect ratio is a basic concept in visual media that defines how wide an image, screen, or video should be compared to its height. This ratio is written as two numbers separated by a colon, such as 16:9 or 4:3. The first represents the width, while the second represents the height. For example, if we have a 16:9 aspect ratio, it suggests that there are nine units in height for every 16 units in terms of width.
Photos
Photography employs aspect ratio as a critical factor in composition and framing. Depending on what cameras or devices are being used, they may have various aspect ratios affecting how images are caught and displayed. So how to find the best ratio?
- 4:3 Aspect Ratio: The 4:3 aspect ratio, commonly used in point-and-shoot cameras and some older digital cameras, closely resembles traditional photograph prints in terms of its shape and is often liked for its balanced composition. The pictures with a 4:3 aspect ratio are slightly wider than high, making them ideal for regular prints and online sharing.

- 3:2 Aspect Ratio: DSLRs shoot at a 3:2 aspect ratio that matches the proportions of 35mm film. This format gives a rectangular frame that offers a wider perspective best suited for landscapes, portraits, and action pictures. It’s balanced between breadth and height, making it suitable for photography.

- 16:9 Aspect Ratio: Widely used for widescreen displays, the 16:9 ratio is perfect for panoramic shots and video content. This aspect ratio provides a cinematic feel and is often used in modern televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones. Photographers use it to create dramatic, expansive images that capture a broad view.

Movies
Filmmaking’s aspect ratio has changed considerably as technology developed over time in response to audience tastes.

- 4:3 Aspect Ratio: It is also called the Academy Ratio. Early cinema and television used 4:3 as their standard. This was almost square, widely used in classic films and TV shows until the middle of the last century. Though it provided a comforting, familiar experience of watching, it lacked the depth that came with wide-screen formats.
- 16:9 Aspect Ratio: The 16:9 aspect ratio became a standard for HDTV and online streaming services as widescreen content gained popularity. This format has a wider field of view, improving the cinematic feel and allowing for more dynamic compositions. Today, it’s mostly used for video content such as TV series, films, or YouTube videos.
- 21:9 Aspect Ratio: This is known as ultra-widescreen or anamorphic format employed to create an immersive theater-like feeling in modern movies. Compared with 16:9 ratios, this aspect provides even wider views; thus great for epic landscapes and big action scenes. It is popularly seen in many blockbuster movies and is increasingly embraced in privileged homes.
Videos
Different video platforms prefer different aspect ratios based on their target audience’s devices used to consume them.
- YouTube (16:9): YouTube has always been associated with 16:9 aspect ratio screens. In this respect, it is similar to most modern display types. This approach eliminates the black bars on the sides of a video so you can watch it without distraction. Therefore, content creators use a 16:9 ratio for shooting and editing their videos.

- Instagram Stories (9:16): Instagram Stories are designed to fill up the entire screen vertically, resulting in an immersive experience on mobile phones. This makes it best for short vertical videos and permits makers to utilize maximum screen real estate.

- Facebook (1:1 and 4:5): Facebook, on the other hand, accepts videos in different ratios, but these two formats, square (1:1) or vertical (4:5) are commonly used ones used for feeds. These were chosen as ideal options, considering that over half of users use smartphones to access this platform. Square videos fit perfectly into desktop and mobile versions while taking less space on the mobile screen, thus attracting more attention.

Part 2: The Aspect Ratio Battleground: TVs vs. Movies
Aspect ratios have been a battleground in visual media history, especially between television and movies. The changes in technology, viewer preferences, and the ongoing search for better viewing experiences are behind developments witnessed in these aspects over time.
Historical Conflict: TV Aspect Ratios (4:3) vs. Movie Aspect Ratios (Widescreen Formats)
These days, the television and film industries both used to have a 4:3 aspect ratio. But soon, filmmakers began using wider ratios such as 2.35:1 and 2.39:1 to bring about a more immersive experience. This transition caused problems for television, which stayed with the 4:3 format for many years.

The Concept of "Letterboxing"
Widescreen movies were preserved on 4:3 TVs through “letterboxing.” The original film’s aspect ratio was maintained by including black bars at the top and bottom of the screen. Thus enabling viewers to see an entire image with no distortion but, at times distracting with strips of black.

"Pan and Scan" Technique
Pan and scan was another technique that cropped widescreen films to fit into 4:3 screens. Important parts of scenes were manually selected by an operator who frequently panned in synchronization with action taking place. Even though no black bars existed, this method frequently resulted in the loss of significant visual materials or compositions being changed, thus distorting the filmmaker's idea.

The Shift to Widescreen TVs
The advent of widescreen televisions, typically having a dimensional ratio of 16:9, represented a major change. These TVs were better suited for showing widescreen content so that letterboxing and pan and scan, became less necessary. As high-definition (HD) content became more popular, this shift coincided with making the proportion of 16:9 become a new standard for TV transmissions and home video formats.
Impact on Content Creation and Consumption
The evolution from 4:3 to widescreen has significantly impacted how content is produced and consumed. Filmmakers and content creators now have more options for aspect ratios that enrich visual experiences. On the other hand, Widescreen TV monitors allow viewers to see content as intended without compromising old techniques.
Part 3: Modern Aspect Ratios: A World Beyond 16:9
Aspect ratios also change with technology and viewing tastes. The 16:9 ratio was groundbreaking a while ago, but it is now standard for HDTVs, computer monitors, and most streaming platforms. Nevertheless, there is an increasing shift in preference towards even wider formats like 21:9 that deliver an even more engaging experience.

There are several reasons why the 21:9 aspect ratio or ultrawide screens are so popular, including:
- Enhanced Immersion – A wider field of view can make movies as well as video games and even everyday computer usage feel more immersive. It allows people to embrace a panoramic vision that fills most of their peripheral vision, thus making it cinematic.
- Productivity – Displaying two windows side by side on a 21:9 monitor is very useful when working and multitasking without having multiple monitors
- Gaming – Gamers love the increased field of view possible when playing with a wider screen, allowing them to participate in many games competitively, overseeing their surrounding environments better than normal aspect ratios can offer.
IMAX and Its Unique Aspect Ratio
Approximately 1.43:1 and 1.90:1 are the aspect ratios used by IMAX theaters, making them taller than the conventional wide screen formats, yielding an image toweringly high and enhancing vertical scenes to give viewers the feeling of being part of an act.

- IMAX Ratio 1.43:1: A near-square format used in some of the largest IMAX theaters and film cameras. It provides a towering image that can make viewers feel as though they are part of the action.
- IMAX Digital Ratio 1.90:1: This slightly wider format is more common in digital IMAX theaters but still offers a larger image than standard 16:9 screens.
Choosing the Right Aspect Ratio
To ensure your content looks its best on the intended platform, choosing the right aspect ratio is important. Here’s a summary of popular aspect ratios and what they’re used for:
- 16:9 – Suitable for HDTVs, computer monitors, and most online video platforms; versatile and widely supported ratio for various types of content.
- 21:9 – Ideal for ultrawide monitors and cinematic experiences; this ratio has gained popularity with gamers and owners of immersive viewing setups.
- IMAX Aspect Ratios (1.43:1 & 1.90:1) Used in IMAX Theaters for Larger-than-Life Experience: these ratios are less commonly seen outside IMAX but essential to that viewing environment.
Part 4: Choosing the Right Fit: Aspect Ratios for Popular Platforms
Here is a brief guide regarding aspect ratios and common platforms:
| Platform | Recommended Aspect Ratio | Reasoning |
| YouTube | 16:9 | It matches the most widescreen TVs to maximize the watching experience. |
| Instagram Feed | 1:1 or 4:5 | The square format prioritizes mobile-first, while 4:5 allows for more vertical space. |
| Instagram Stories | 9:16 | It has been optimized for portrait-oriented mobile viewing. |
| Facebook Feed | 16:9 or 4:3 | Both formats are fine; only 16:9 gives more room to view images. |
| Twitter Feed | 16:9 or 1:1 | Square format performs well even as it provides extra room for wider images compared to other formats like 16:9. |
Part 5: Beyond the Basics: Advanced Aspect Ratio Considerations (Optional)
In creating videos, it is essential to know “safe zones.” These frame parts will be seen on any screen regardless of its aspect ratio or overscan. There are two types of safe zones:
- Title Safe Zone- This margin guarantees that text and important information will never disappear from appearing in any display. It usually comprises about ten percent inward from the edges of the frame area.
- Action Safe Zone- This margin ensures that all critical action remains visible. It generally comprises about five percent inward from edges on all sides of the frame area.
Keeping your content inside these safe zones is important because it ensures you maintain a professional look and that viewers see everything they need, regardless of screen size or aspect ratio.
Aspect Ratio Adjustments with Software Tools
Advanced video editing often includes adjusting the aspect ratio to suit various platforms or artistic intuitions. Such software tools as Wondershare Filmora simplify the process. Wondershare Filmora is an intuitive video editing tool for beginners and professionals. Here are some of these advantages:
- User-friendly Interface: Even if you have no skills in video editing, you can start your work with Filmora, which has a drag-and-drop interface.
- Powerful Features: With keyframing, motion tracking, and color grading, Filmora can create professional videos, but still, it is simple.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: No matter the platform it will be shared on, filmora allows you to make anything look good by supporting different aspect ratios and resolutions.
Steps to Use the Crop Tool in Wondershare Filmora
Step 1: Import Your Video
Open Wondershare Filmora and create a new project. Click on “Import” to list your media files on the media library after selecting your source file from its location. Take this video file from the media library onto the timeline below.
Step 2: Select the Video Clip
Highlighting that clip implies that it is selected when you click on it in the timeline; this will show that the clip was highlighted.
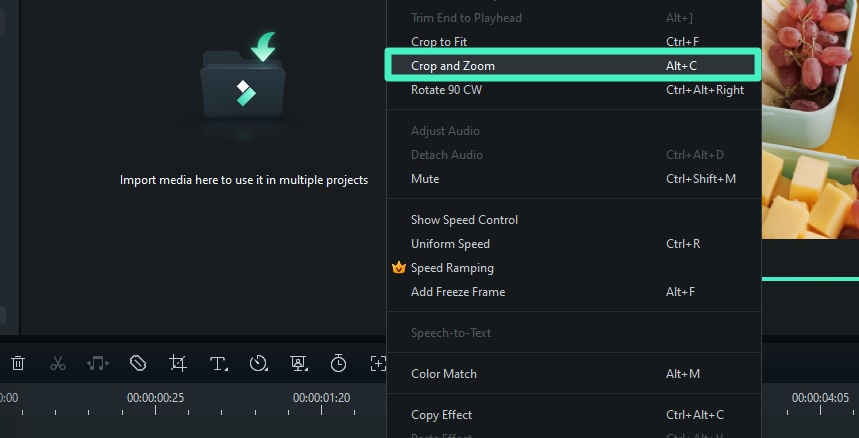
Step 3: Open the Crop Tool
Select ‘crop and zoom’ from the context menu after right-clicking at the timeline’s video clip, or press the ‘crop and zoom’ icon (a crop symbol) above the timeline.
Step 4: Adjust the Crop Area
When you press the Crop and Zoom button, you will see your video in a resizable rectangle overlay window. You can change the shape and position of the rectangle to focus on just the parts of the video that you want to keep. The rest of the video outside this box will be cut.
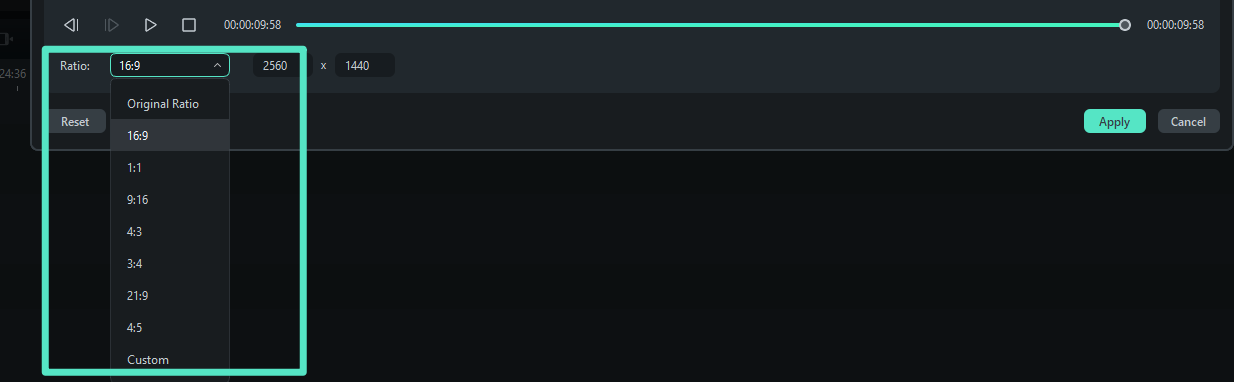
There are various preset aspect ratios like 16:9, 4:3, and 1:1, which can be applied, or you may go ahead and manually adjust this rectangle for custom cropping.
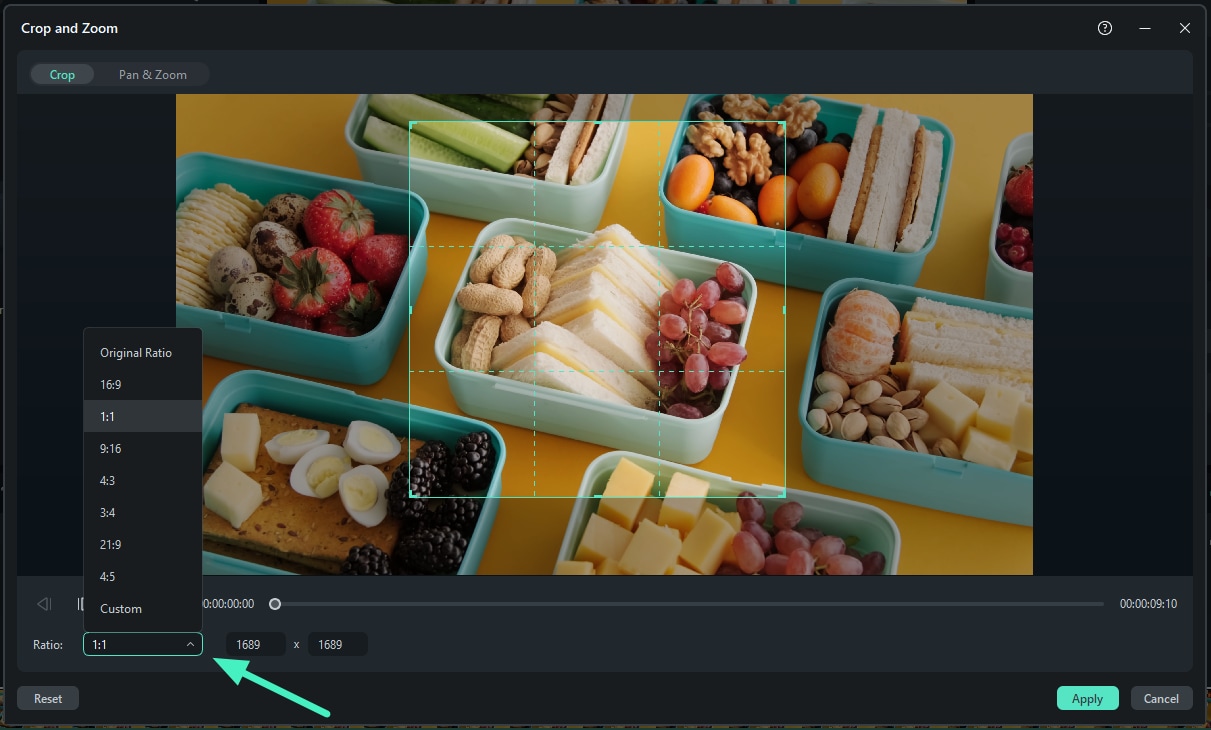
Step 5: Apply the Crop
After setting up the crop area, click OK to apply it. As a result, all clips in the timeline will show cropped areas on them.
Step 6: Preview and Fine-Tune
Watch your cropped work by placing it within the preview. Should there be any need for further alterations, one can redo cropping easily.
Step 7: Export Your Video
After cropping, you can continue editing your video or export it.
For exporting, click “export,” then choose format and settings before clicking “export” again to save a final video clip.
Conclusion
Knowing the aspect ratio is necessary when creating attractive content across media types. The aspect ratio influences how your audience experiences your work, from photography and movies to modern video platforms. Using tools like Wondershare Filmora choose an appropriate aspect ratio easily. By mastering aspect ratios, you can ensure your content looks its best.



 100% Security Verified | No Subscription Required | No Malware
100% Security Verified | No Subscription Required | No Malware

