In this article
Understanding Video Formats
Every digital video has a structure that determines how it is stored and played. While some compress better, others deliver higher quality, and a few require you to do advanced editing. This is why, as a video producer, you need to understand "what is video format".
This guide breaks down the essential aspects of formats and codecs to help you discover the best video file format. Read on.

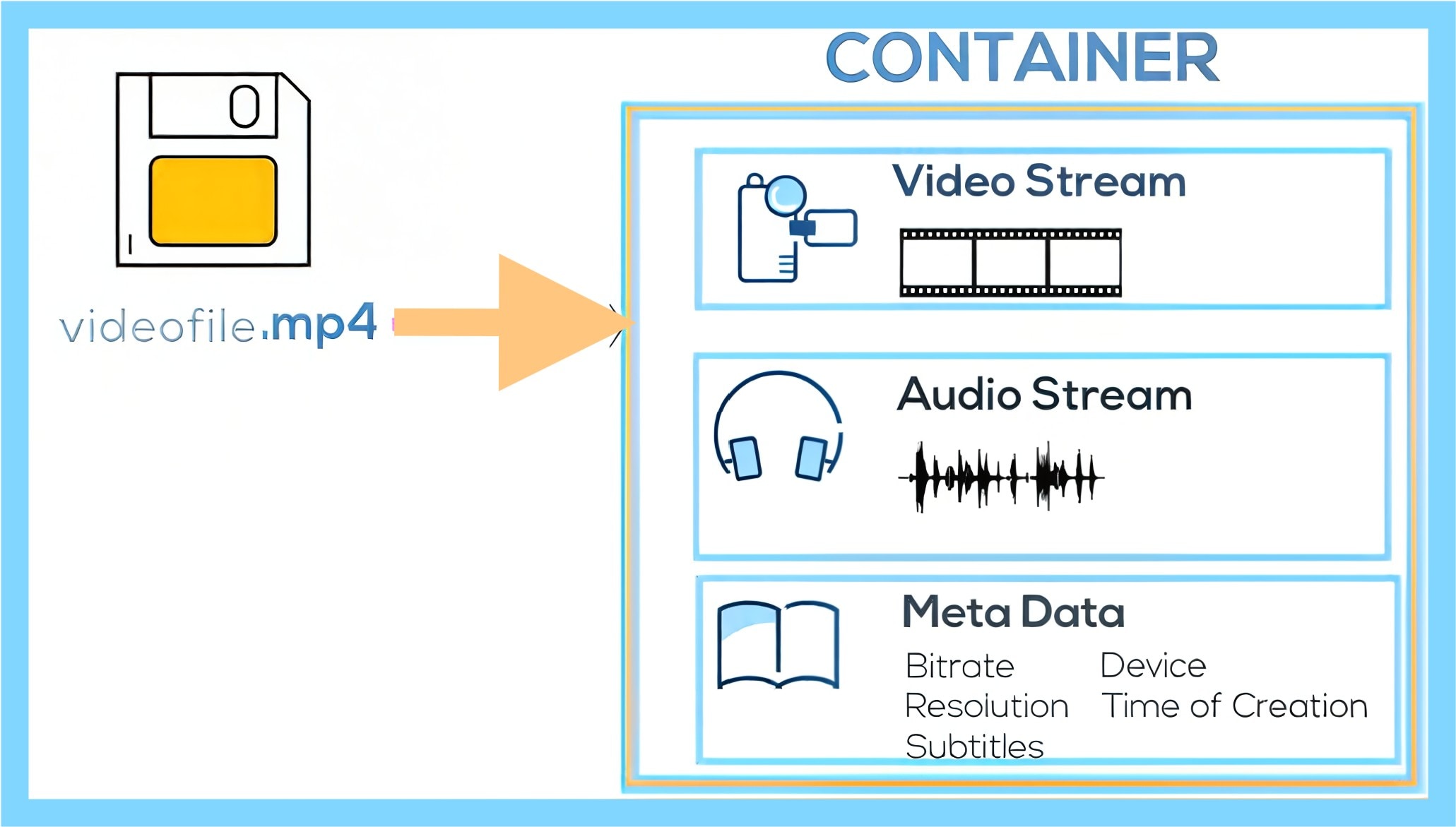
A video format is the digital structure that helps in packaging your video, audio, and supporting data. It arranges the data in a single file, then acts as a wrapper that holds the components together. Helpfully, this ensures they remain synchronized during playback or editing.
Some types of video formats offer you better compression, while others preserve higher resolution. But you need to understand the core elements to know how to choose the best video format.
Key Elements of Video Format
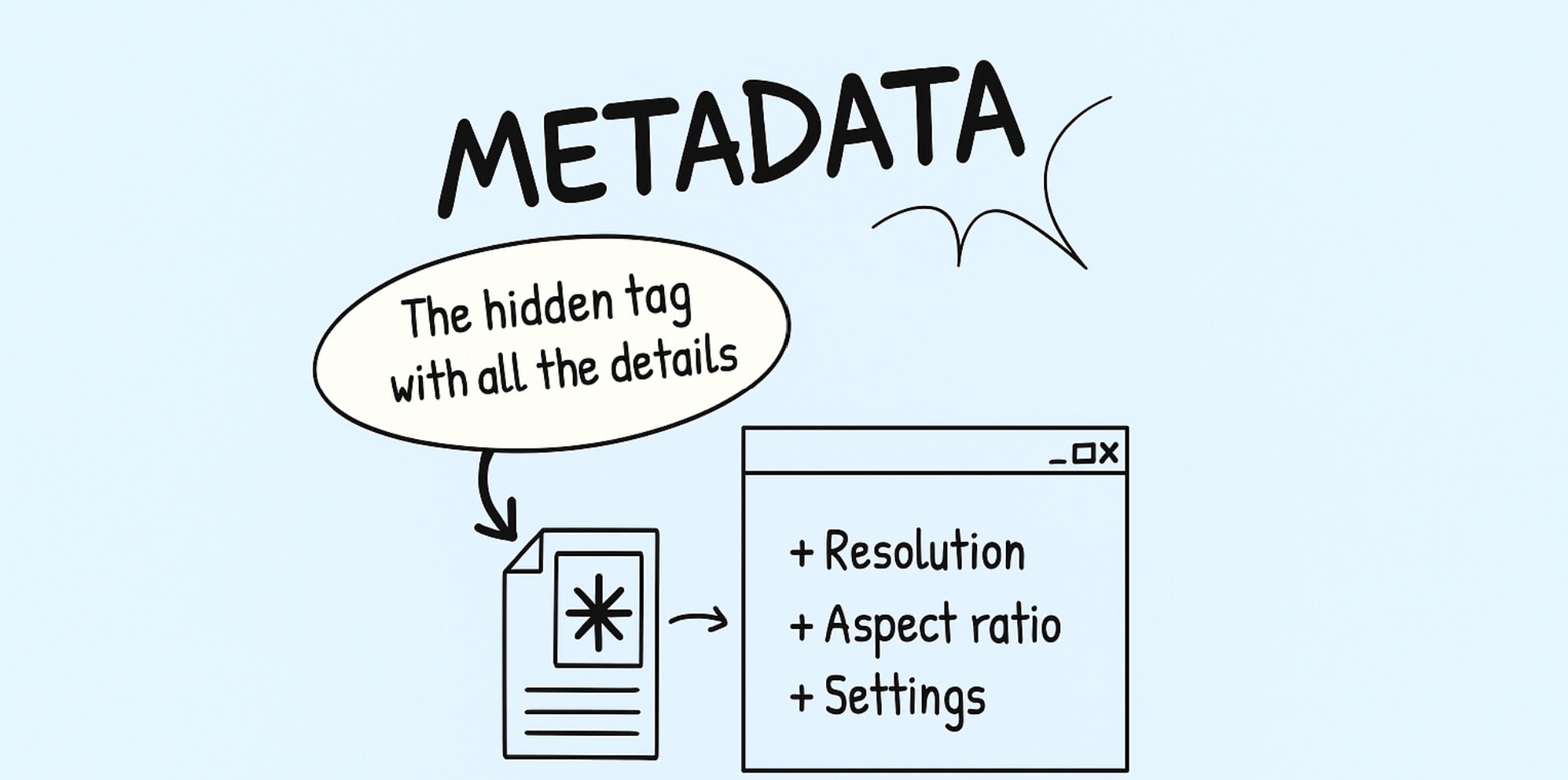
Let's say you've just finished editing a video. It looks sharp and sounds clean. But when you send it to your friend, it won't play. That's a format issue, and can be traced to these three elements: the container, the codec, and the metadata.
Video Formats vs. Codecs: How Do Video Formats Differ from Codecs?
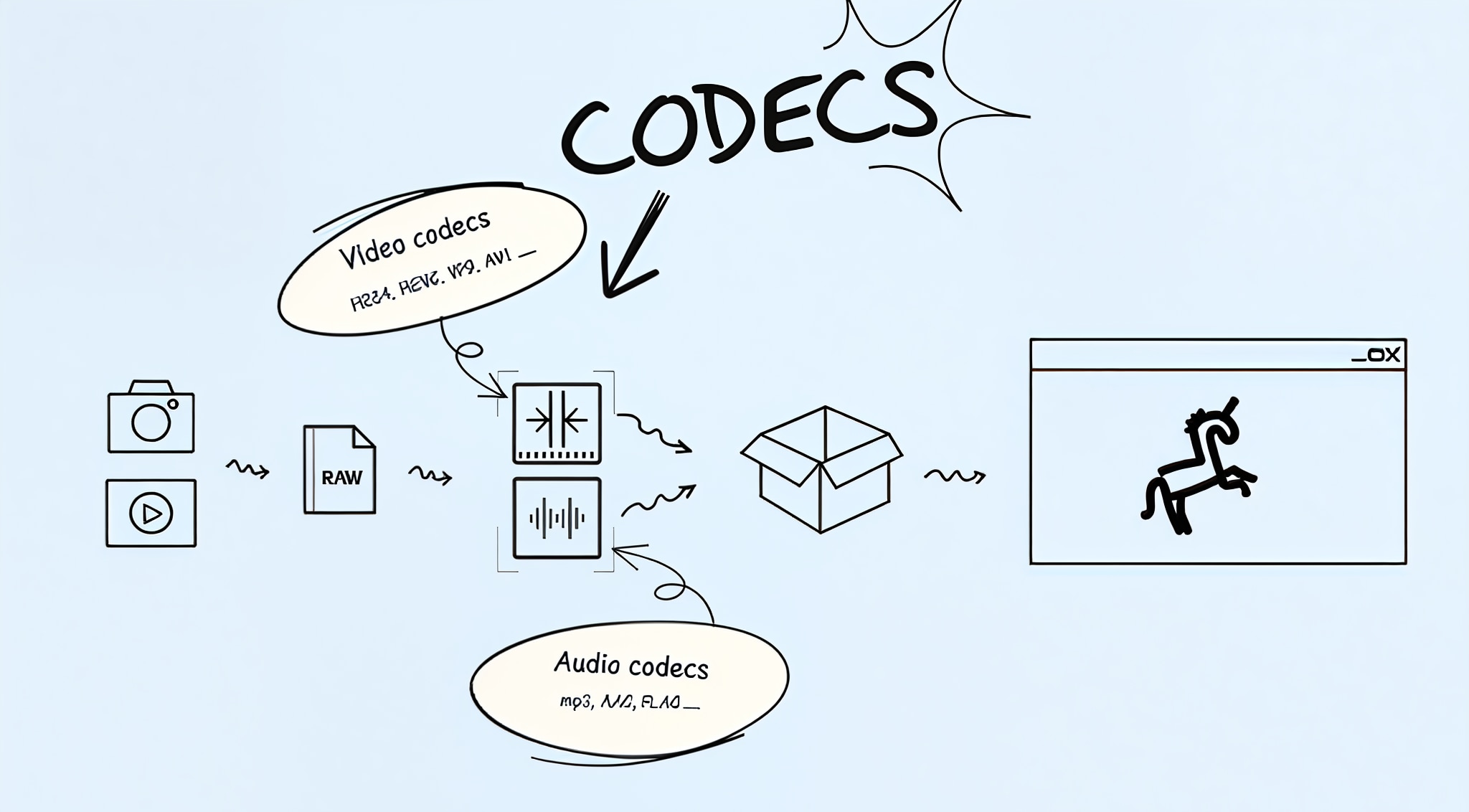
A video format holds your video, audio, subtitles, and even metadata in one neat package, while the codec compresses and decompresses the video inside that package.
Formats like MP4, MOV, and AVI define how the file is structured and plays across different devices. But each of these formats supports different codecs, such as H.264, HEVC, VP9, or AV1.

Your clip format might load fine, but if the codec's off, the video stutters or looks blurry. You might hear the sound, but the screen freezes. So when you pick a video format, check which codec it uses. That small step saves you a lot of frustration.
The table below provides a clearer answer to the question "How do video formats differ from codecs?"
| Aspect | Video Format (Container) | Codec |
| Function | Stores video, audio, metadata, and subtitles. | Compresses and decompresses media streams. |
| Examples | MP4, MOV, MKV, AVI. | H.264, HEVC, VP9, AV1. |
| Controls | Determines compatibility, compression, and playback behavior. | Compression rate, quality, and file size. |
| Can it be changed? | Yes, during export or conversion. | Yes, but the codec must match the target format. |
How Bitrate and Resolution Affect Your Video Format Choice
Bitrate controls how much data gets processed each second, while resolution deals with how many pixels appear in every frame. So, how do they actually affect your video format?
You've probably seen a crisp video that still plays like a slideshow. That's often a bitrate issue, not just resolution. Your video might be 4K, but without enough bitrate, it turns into a blurry mess. Using a low bitrate might help shrink the file size, but it can also lead to pixelation, especially during fast movements.
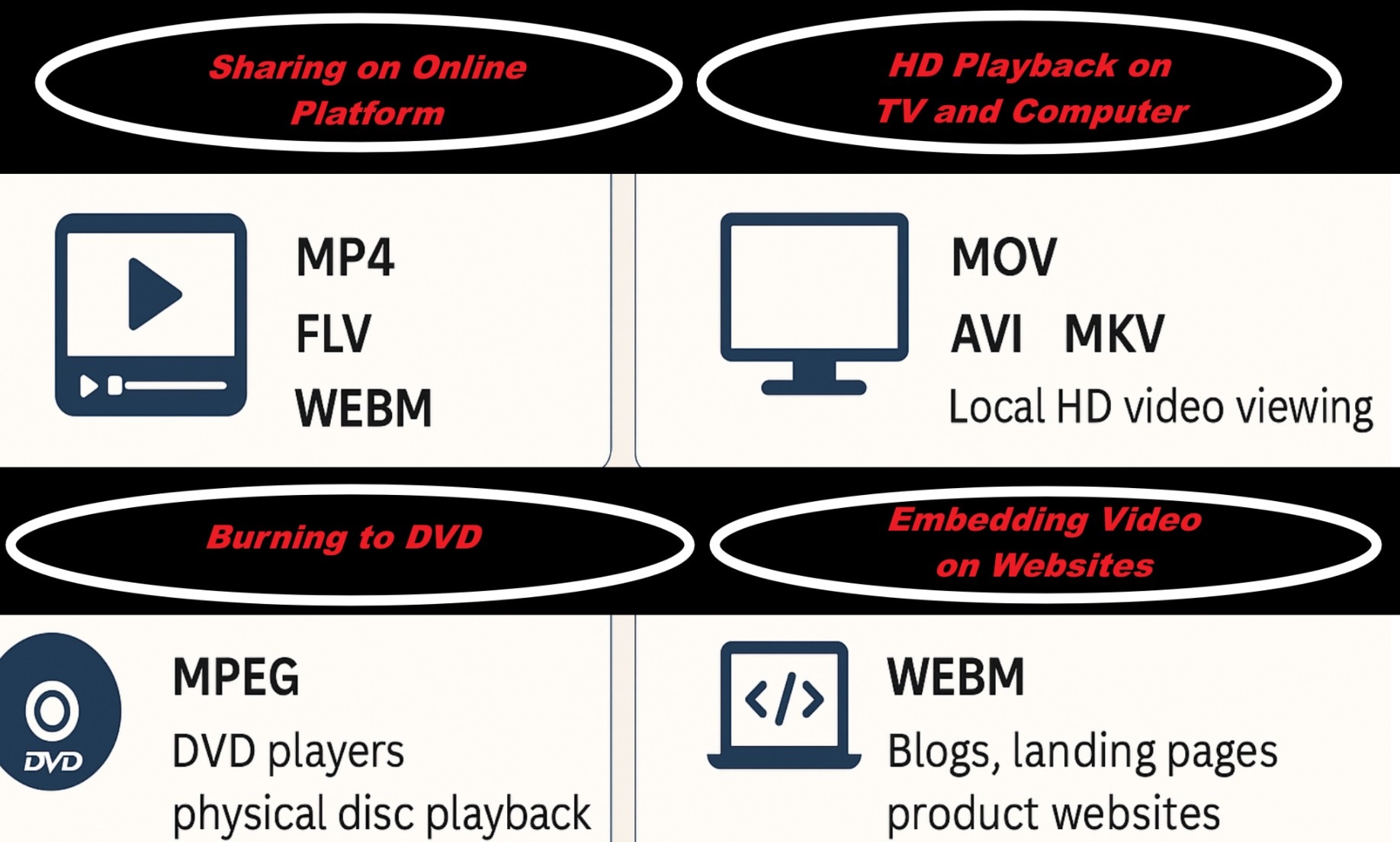
Comparison of Popular Video Formats

Choosing the best video file format will help you avoid quality loss and ensure smooth delivery. When format, codec, and platform align, the result is both efficient and professional.
The table below compares key formats based on use case, resolution, size, and ideal codec.
| Video Format | Best Use Case | Device Compatibility | Max Resolution | File Size | Ideal Codec |
| MP4 (.mp4) | Online sharing, social media, and mobile playback | Virtually all devices: phones, tablets, TVs, PCs, and web browsers | 4K | Small to Medium | H.264, H.265 |
| MOV (.mov) | Professional editing, Apple workflows | Native on macOS, iPhone, iPad; requires QuickTime or plugins on Windows | 8K | Large | ProRes, H.264 |
| AVI (.avi) | Legacy playback, Windows editing | Strong support on Windows and cross-platform via VLC/multipurpose players | 1080p | Large | DivX, MJPEG |
| MKV (.mkv) | High-quality archiving, subtitles | Supported by VLC, Plex, Windows, macOS, Linux | 4K | Medium to Large | H.264, VP9 |
| WMV (.wmv) | Windows streaming, email delivery | Native on Windows, requires plugins or apps on macOS and Linux | 1080p | Small | WMV9 |
| FLV (.flv) | Flash-based video content | Supported by legacy Flash players; now limited in modern browsers | 720p | Small | Sorenson-Spark |
| GIF (.gif) | Short loops, memes | Universal support across web, messaging apps, and all devices | 480p | Very Small | Frame based |
| WEBM (.webm) | HTML5 video, modern web embedding | Native in Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Android browsers | 4K | Small | VP8, VP9 |
| AVCHD (.mts/.m2ts) | HD camcorder recording, Blu-ray content | Supported on Sony/Panasonic camcorders, Blu-ray players, and desktop software | 1080p | Medium | H.264 |
Common Video Formats Used in Popular Media
How to Choose the Best Video Format
When choosing the best video format, always match compatibility to your target platform. MP4 with H.264 remains the all-around choice for smooth playback and wide device support. If you need maximum quality or support for advanced workflows, opt for formats like MOV (with ProRes) or MKV for editing and archiving.
Top Video Format Mistakes That Ruin Quality and Compatibility

Mistakes in choosing or managing video formats can prevent playback, distort images, or reduce resolution across platforms. Below are the 3 top mistakes you should not make.
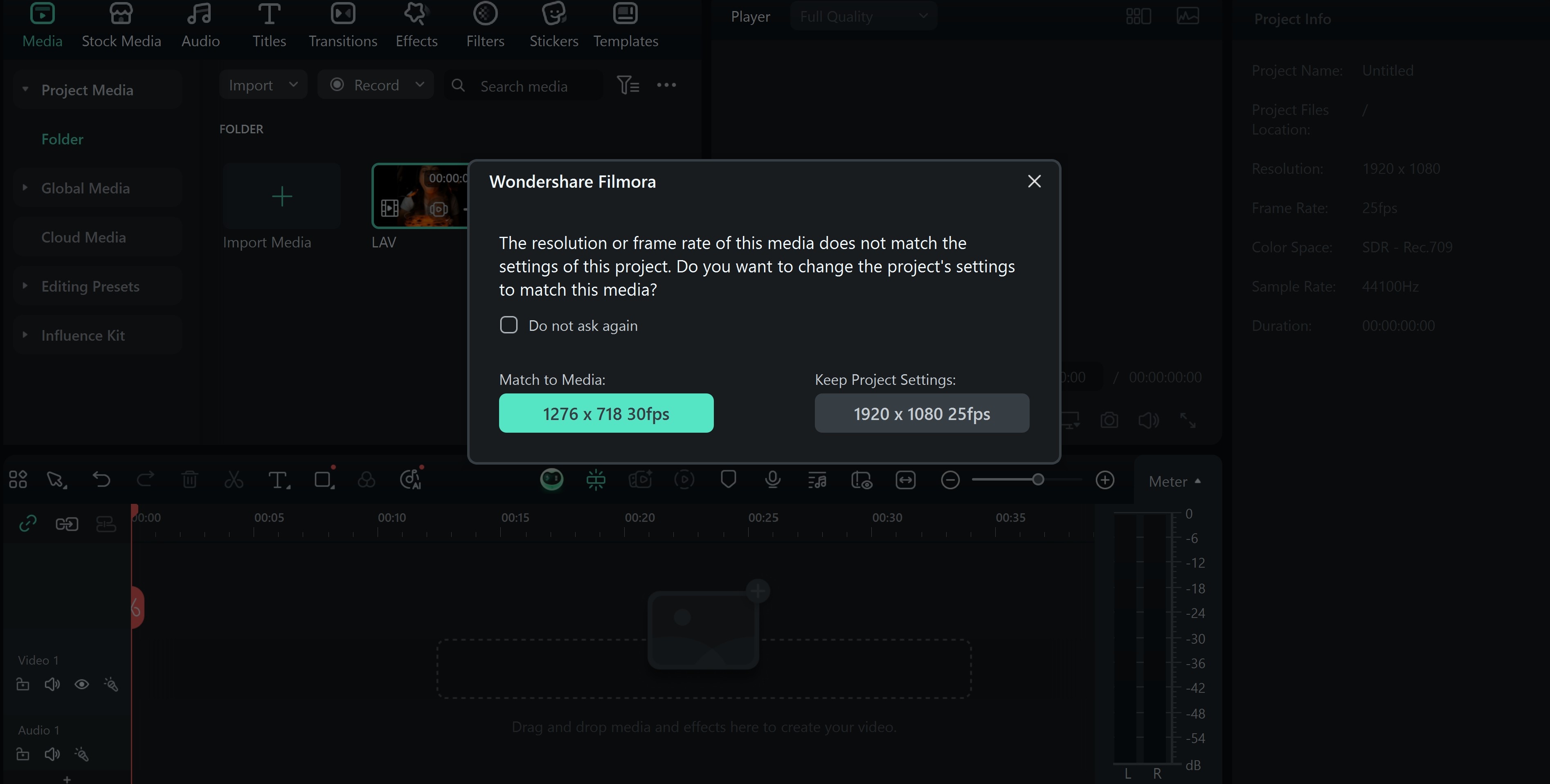
How to Convert Video Format and Export Using Filmora

Filmora provides users with a simple method to convert video formats. This helps you to avoid compatibility errors while maintaining high video quality. Here is how you can get this done.
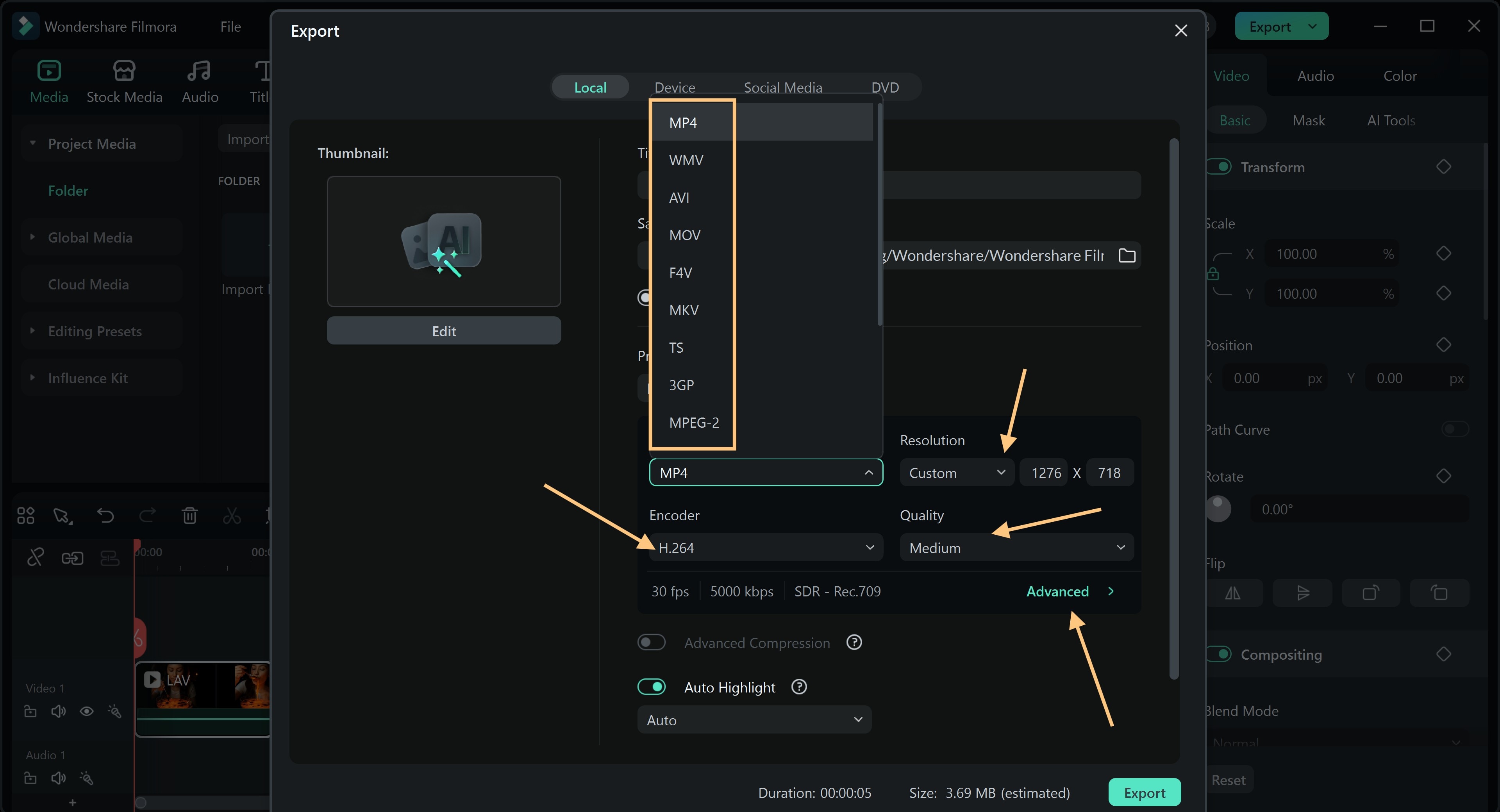

Pro Tips: Choosing the Right Format in Filmora
Selecting the right video format in Filmora improves both output quality and playback performance. Each format serves a different goal, and knowing when to use each makes editing more efficient.
| Medium | Best Performing Formats | Key Features |
| Mobile Devices | MP4 (H.264), MOV | Natively supported on Android/iOS, fast loading, efficient compression, high compatibility |
| Desktop | MP4 (H.264), WebM, MKV | Broad codec and container support, plays in browsers and editors, handles high resolution |
| Broadcast | MXF, ProRes, DNxHD | High bitrates, supports multi-audio and metadata, minimal compression, used in professional TV/film production |
Conclusion
Understanding how bitrate, resolution, and codec interact with your chosen video file format helps you make the right choice. If you mess one up, your video might buffer, shrink, or refuse to open.
Nevertheless, Filmora saves the day when format issues pop up. It supports many video format types and lets you save in the format you prefer.
FAQ
-
Why are some video formats larger than others?
File size depends on the video format, codec, resolution, and bitrate used. When the bitrate is high and compression is minimal, the file size becomes larger. -
Can you change a video codec without changing the format?
Yes, the codec can be changed inside the same video format container. For example, an MP4 file can use H.264 or HEVC as the codec. However, the new codec must remain compatible with the chosen video file format, or playback may fail on some platforms. -
Which video formats have the highest quality?
MOV and MKV are known for preserving high-resolution and lossless detail. These video formats support advanced codecs like ProRes and VP9.





