In this article
Understanding Digital Rights Management
Have you ever found yourself in a situation where you want to play a video and you are met with a pop-up saying that you need to sign in or update your permissions? This is not accidental at all. It's Digital Rights Management (DRM) in action. DRM refers to a set of controls designed to protect media, manage access, and track usage across devices and platforms. From subscription streaming services to e-learning portals, DRM plays a critical role in securing digital content while enabling businesses to monetize their media effectively.
In this guide, we'll explain DRM, how it works, where it's used today, and how you can add your own protective measures using a powerful video editor.

Digital Rights Management is a set of access controls that determine who can view, copy, or share media. Videos are packaged so that you can decrypt and play them with valid licenses.
DRM isn't just about simply locking files. Its purpose goes way beyond security. It supports monetization by enforcing subscription models, rentals, or pay-per-view systems. It enables windowing, where content becomes available in phases across regions or devices. It also controls regioning, letting publishers comply with licensing and distribution agreements in different areas. While these protections are essential for businesses, they also influence user experience, dictating where and how you can access content.
The Technical Side of Digital Rights Management
Behind any play button is a complex workflow of encryption, licensing, and secure playback. Let's take a closer look.
The Core Technologies Behind DRM
The Key Innovations of Digital Rights Management
The Current State of DRM Software
DRM is not an option but a necessity for major streaming providers today. Giants like Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime all rely on multi-DRM setups to secure their content globally. Even smaller publishers now adopt SaaS-based multi-DRM platforms to improve cost efficiency and performance speed. Cloud-based solutions allow them to scale quickly without the cost of building full DRM infrastructures from scratch.
When and Where to Use Digital Rights Management
DRM is a must if your content strategy involves premium assets, regional licensing, or privacy-sensitive material. Let's consider the most common applications.
Real-World Applications for DRM



These were the most common use cases, but rest assured, there are many more.
What Are the Limitations of Digital Rights Management?
Just like any developing technology, DRM does come with some limitations. Here are the most noteworthy options to consider.
But all these challenges pale in comparison to the need for protection, especially when discussing intellectual property and maintaining licensing agreements.
What is the Future of DRM?
In the future, we can expect better integration between DRM, leading to real-time leak detection to combat piracy effectively. Developers will soon manage Widevine, FairPlay, and PlayReady through one orchestration layer, reducing complexity and cost. Also, next-gen DRM frameworks will allow secure offline playback while maintaining stronger device binding to prevent unauthorized sharing. With these advancements, content owners can look to deliver seamless, secure playback experiences without sacrificing performance.
How to Protect Your Video with a Watermark?
If you are working on a video and you want to publish it and keep it secret so that only you have access to the original, you can add a watermark to it using one of the best video editing platforms on the market. It's called Wondershare Filmora, and it actually gives you the option to add animated text to your video and reduce its opacity to create the perfect watermark. If you want to learn how to do it, check out the easy, three-step guide.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Watermarks in Filmora
Before you start following the steps, make sure that you download and install Filmora on your Windows or Mac device, open it, create a new project, and import the video where you want to add a watermark. When that is done, you can jump into the steps below.
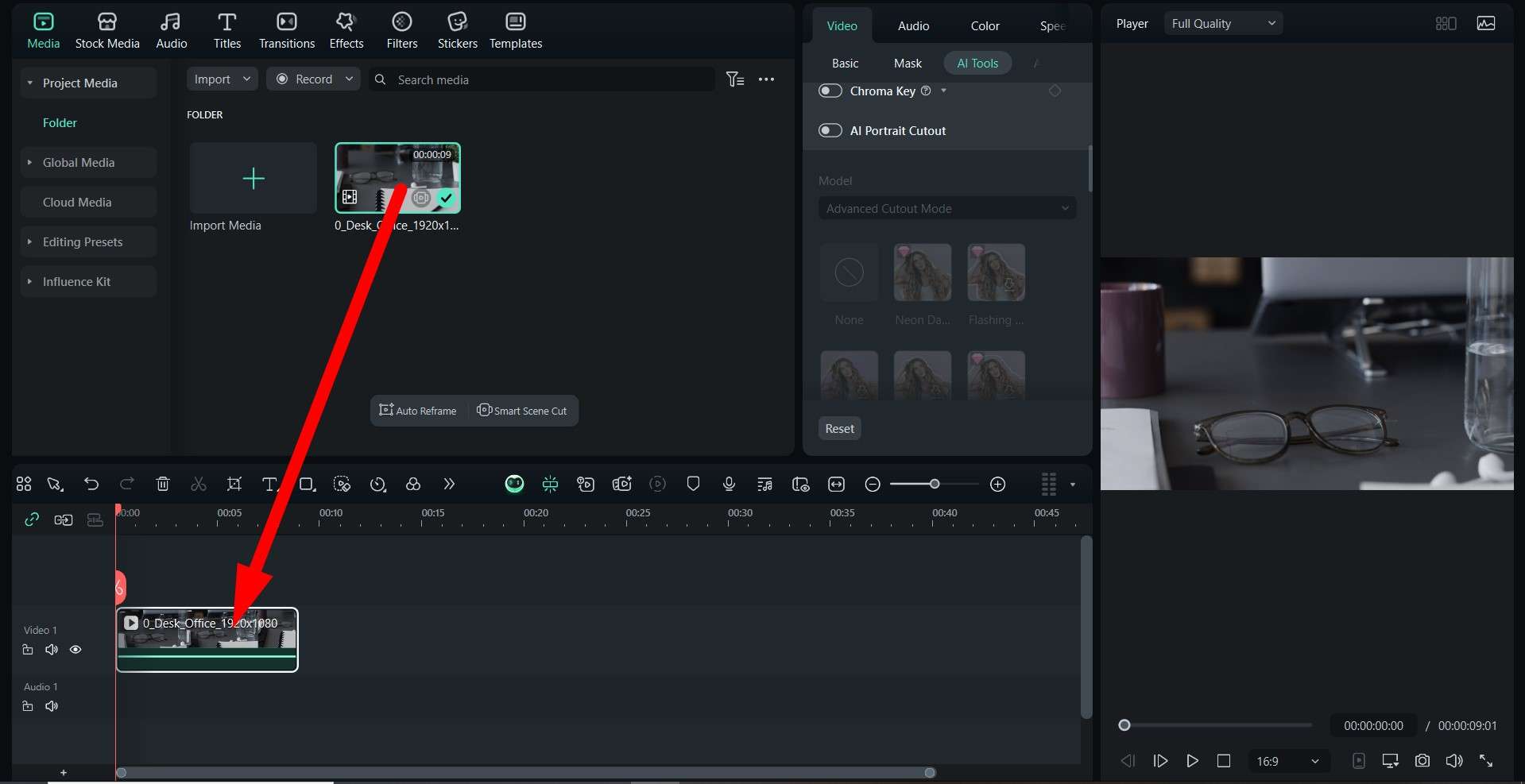
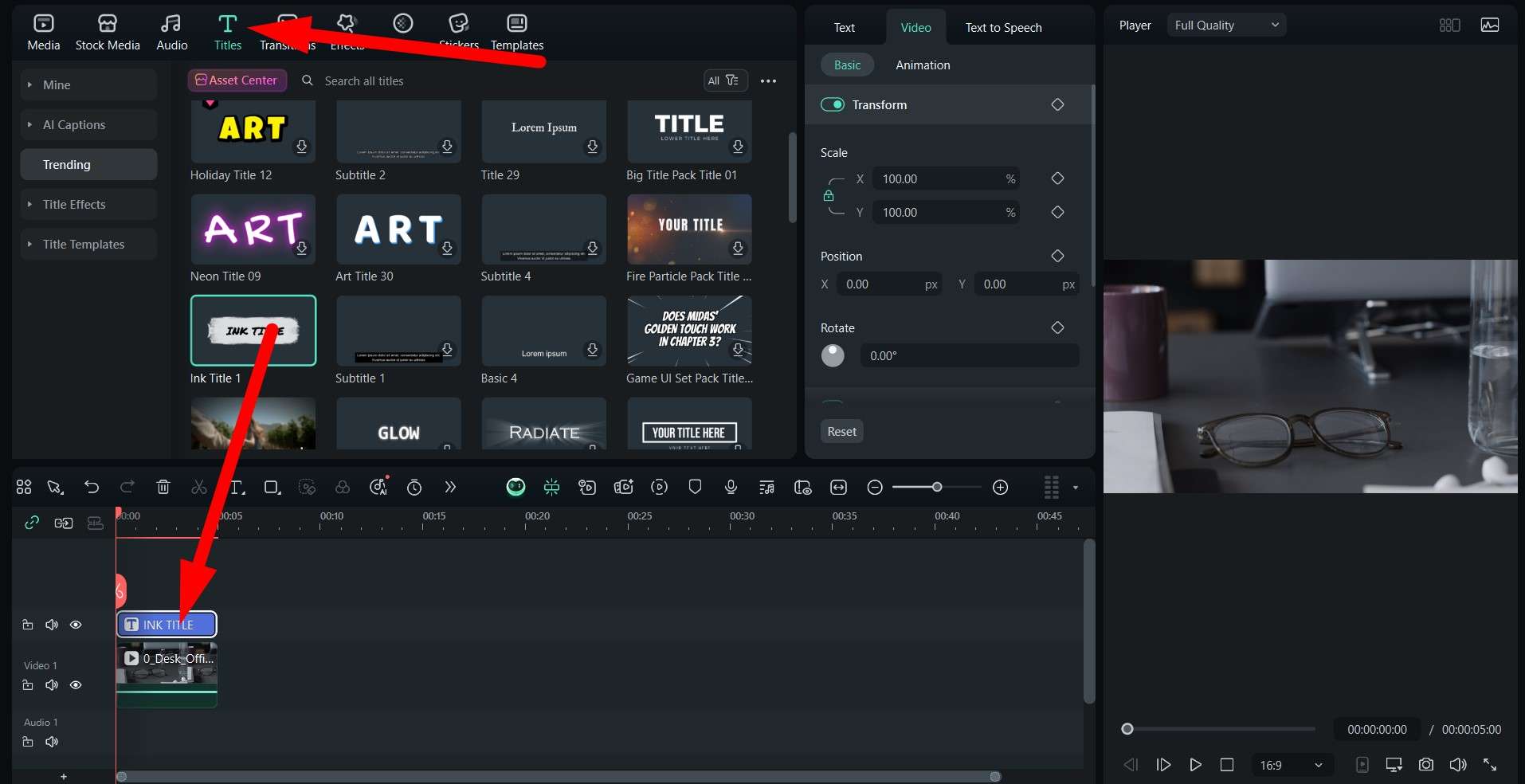
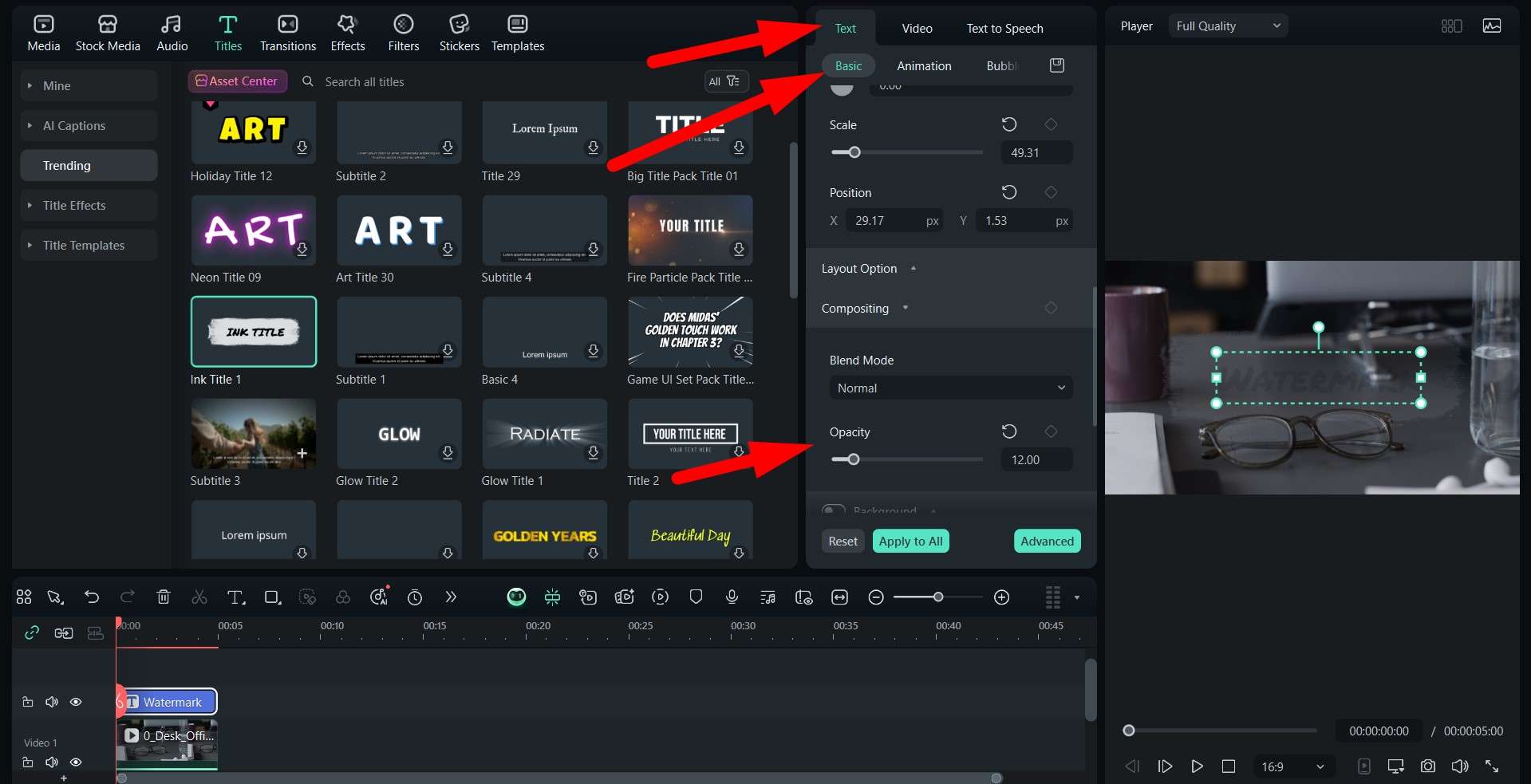

This demonstration shows how easy Filmora is to use. No matter the complexity of the task at hand, Filmora offers easy steps to get the best result. Download the PC version today, and if you want to add digital rights measures to your content on your phone, you'll be happy to find out that Filmora is also available as a mobile app for Android and iOS.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the main purpose of Digital Rights Management (DRM)?
The main purpose of DRM is to protect digital content from unauthorized access, copying, and distribution. It allows content creators and distributors to control how their media is used, ensuring that only authorized users can access it according to the terms set by the rights holder. -
Does DRM only apply to video content?
No, DRM applies to various types of digital content including videos, music, e-books, software, and documents. Any digital content that needs protection from unauthorized use can be secured with DRM technology. -
Can DRM be removed from protected content?
While there are tools and methods that claim to remove DRM protection, doing so is typically illegal under copyright laws in most countries. DRM removal violates the terms of service of content providers and may constitute copyright infringement. -
Why do some users dislike DRM protection?
Some users dislike DRM because it can limit their ability to use content they've legally purchased across different devices, create backups, or access content without internet connectivity. DRM restrictions can sometimes create inconvenience for legitimate users while attempting to prevent piracy. -
Is DRM the same as encryption?
While DRM often uses encryption as one of its components, DRM is broader than just encryption. DRM includes the entire system of access control technologies, license management, and usage restrictions that govern how digital content can be used, whereas encryption specifically refers to the scrambling of content to make it unreadable without the proper key.



