In this article
Understanding 360 Video
360 video has emerged as one of the most engaging formats for immersive storytelling. By capturing an entire environment in all directions, it allows viewers to look around freely as if they were standing inside the scene.
Today, this format is widely recognized across industries, often appearing in marketing, education, tourism, and entertainment. People searching for what is 360 video is usually want to understand how it differs from traditional video and why it has become so popular.

360 video (also called 360-degree video, surround video, or spherical video) refers to video recordings that capture the view in every direction at the same time. This is made possible by using an omnidirectional camera or an array of cameras working together.
The concept of surrounding viewers with visual content has existed for centuries in art and photography, but 360-degree videos only became practical in the digital age with advanced camera rigs, automated stitching software, and platforms that support immersive playback.
Technical Breakdown:
Core Technology:
360-degree videos are recorded with omnidirectional cameras that have multiple lenses pointing in different directions. In some setups, several cameras are mounted together in a rig. Each lens captures a piece of the scene, and then the software stitches the pieces into a full spherical view. The final result is a seamless sphere that lets viewers look around freely.
Key Innovations:
Current State:
Today, 360 video is no longer limited to big studios. Marketers, educators, real estate agents, and independent creators all use it. Easy-to-use editing tools, browser-based playback, and VR integration have made the technology widely accessible. The format continues to evolve, blending with VR and interactive media to deliver even more immersive experiences.
Application Section - When/Where to Use 360 Video
A 360 video is more than just a new way to record footage. It is a tool that transforms how audiences experience stories, products, and environments. From marketing campaigns to classroom lessons, 360-degree videos open the door to engagement that traditional video cannot deliver.
Real-World Applications of 360 Video:
Industry Impact:



Specialized Variants & Use Cases:
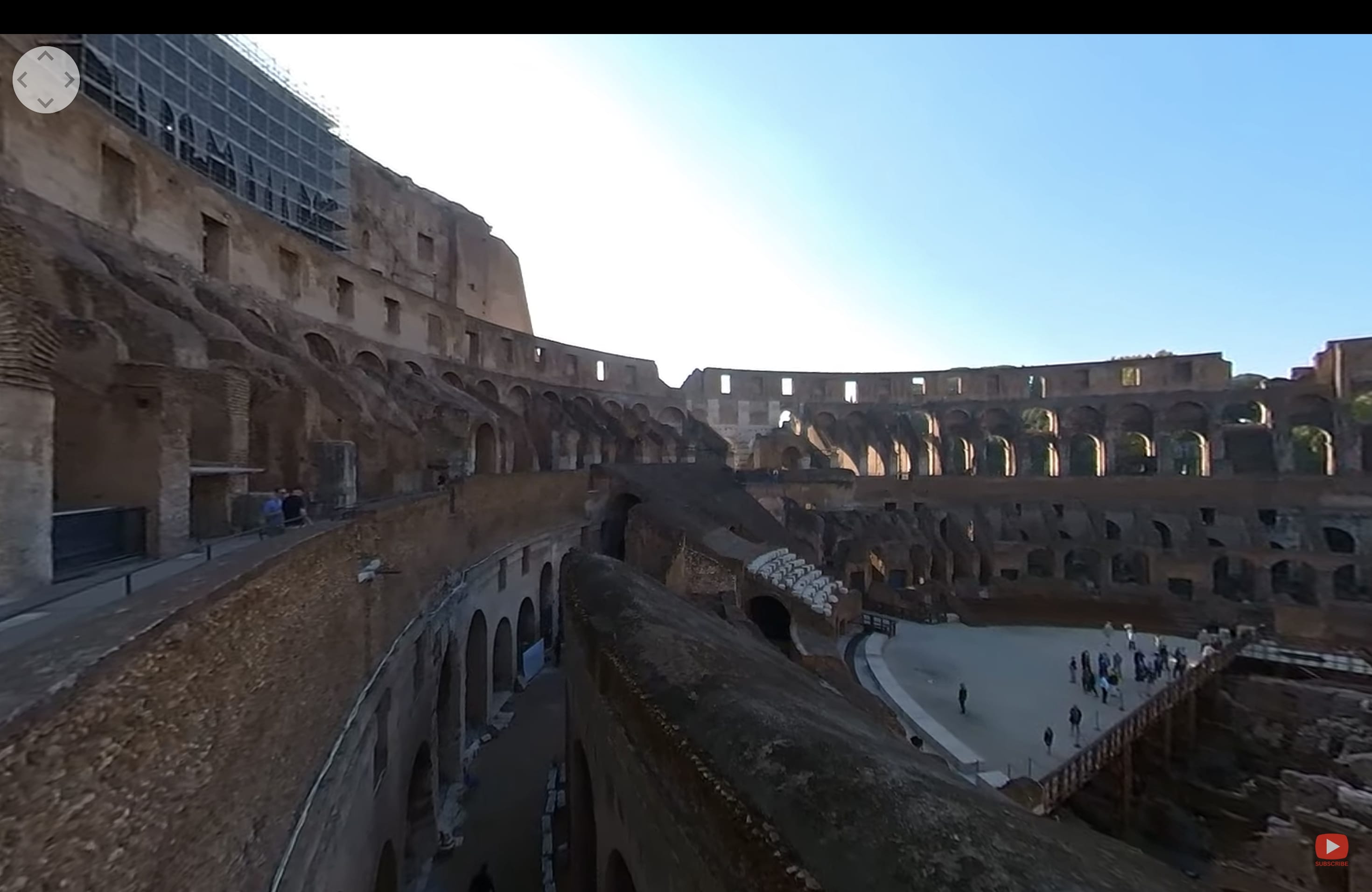
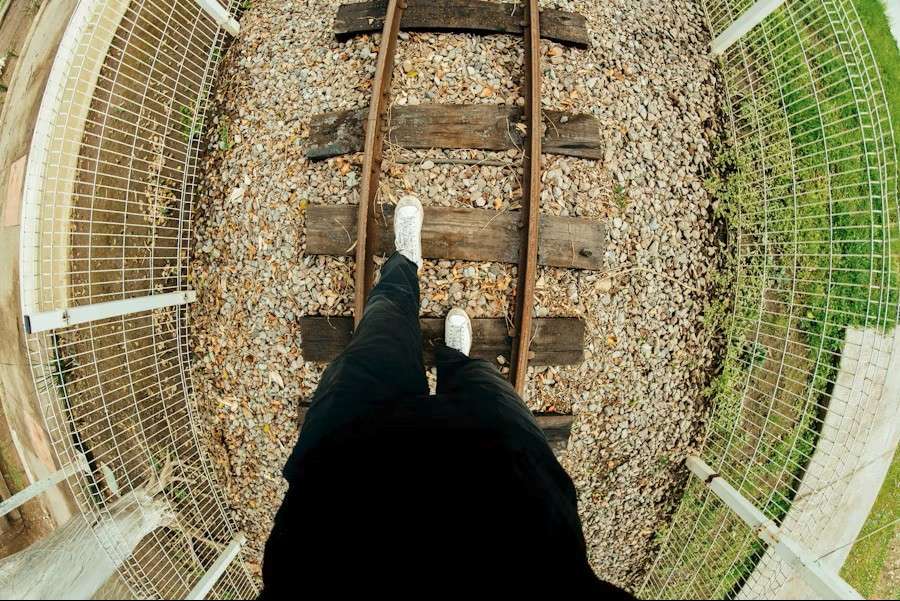


Limitations and Challenges:
Future Outlook:
The next generation of immersive media is already taking shape. Technologies like volumetric video and six degrees of freedom (6DOF) capture will allow viewers not only to look around but also to move inside the scene. Combined with augmented reality and real-time rendering, future 360 content will offer personalized and lifelike experiences. This will expand the role of 360 video in education, entertainment, and business even further.
Practical Demonstration Section - How to Use 360 Video
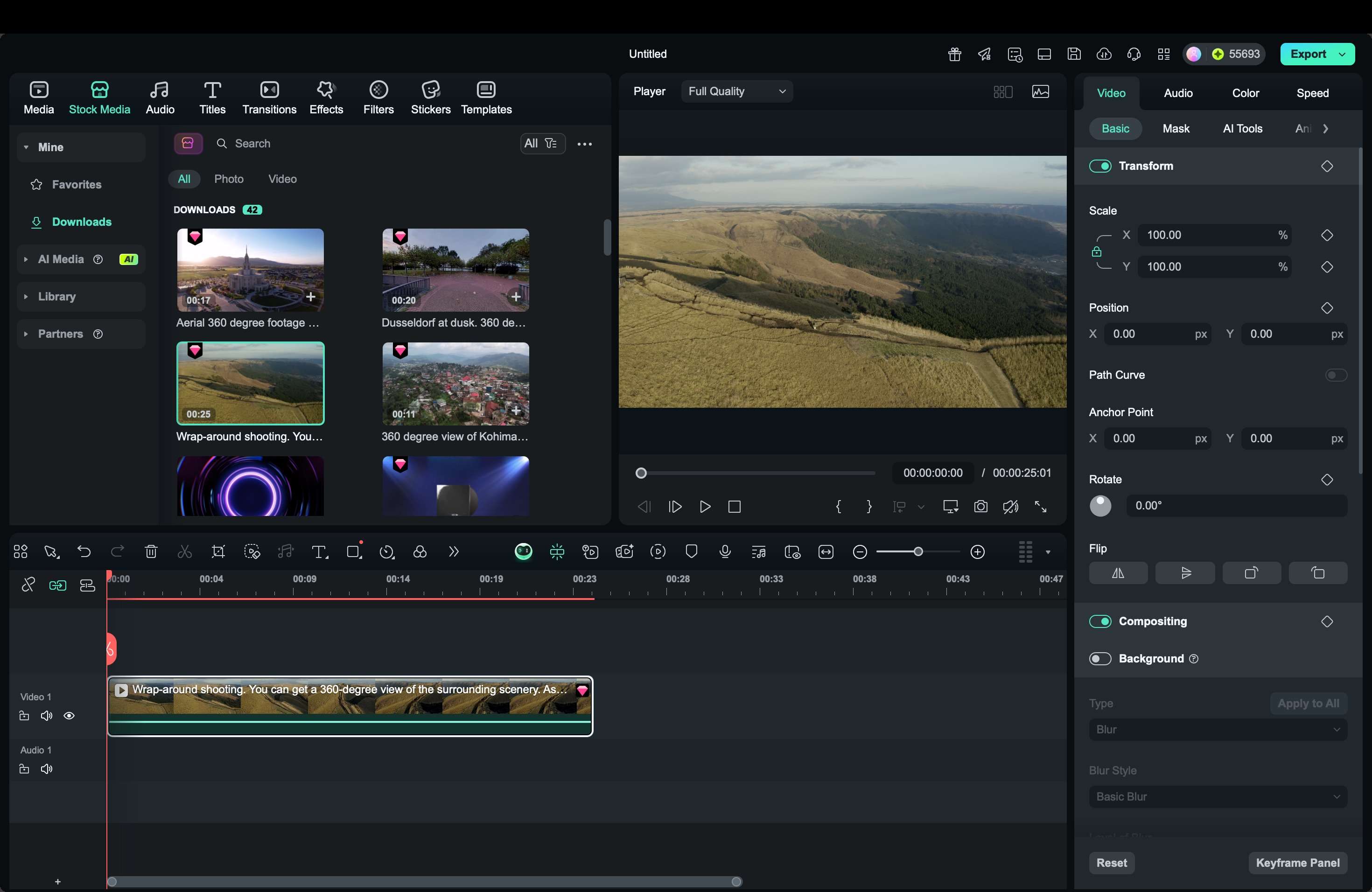
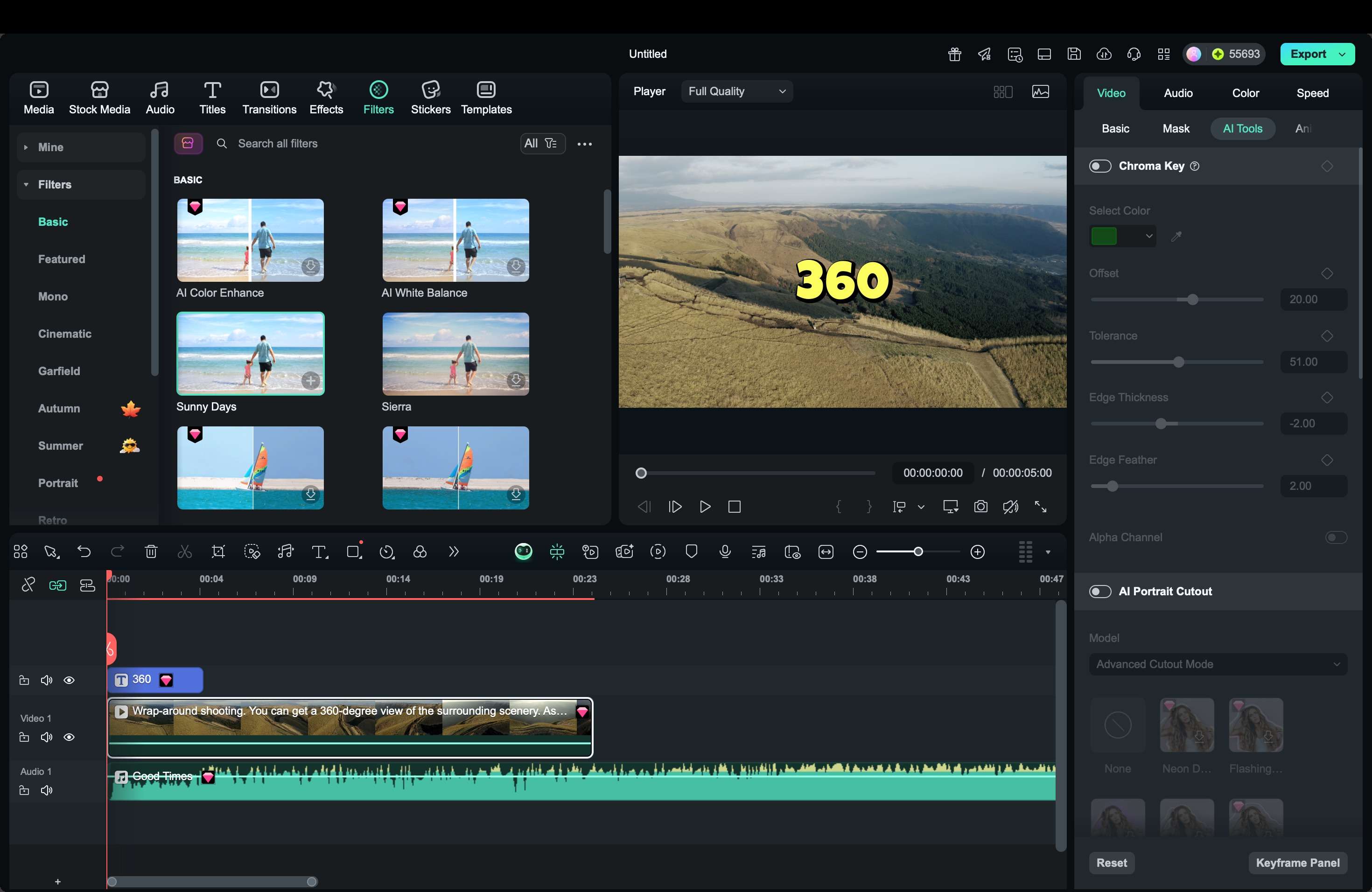
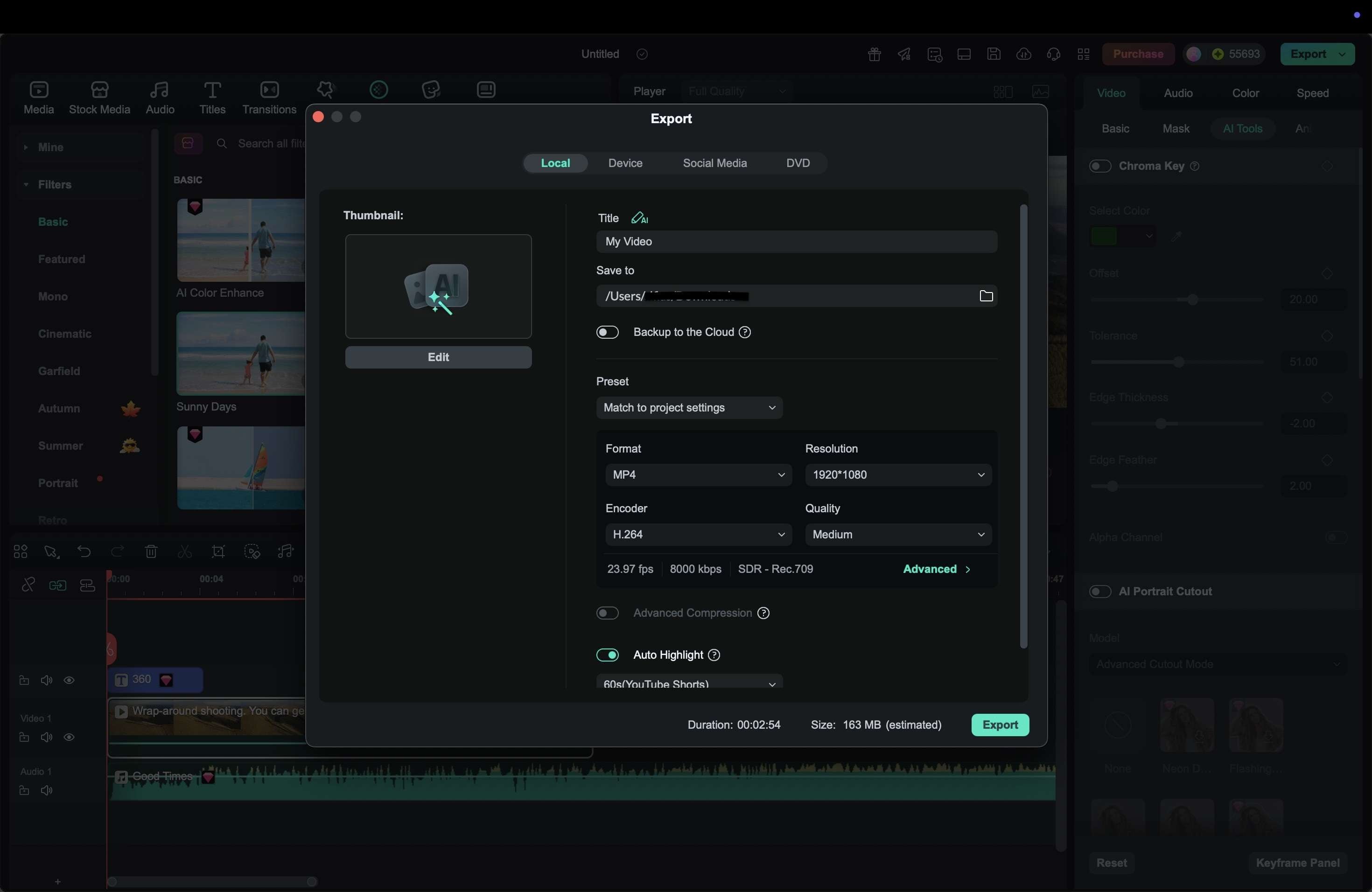
Editing 360-degree videos requires software that can properly handle spherical footage. Without the right tools, the video may appear distorted or lose its immersive effect. Wondershare Filmora offers a practical solution for both beginners and intermediate creators. It supports equirectangular video formats, keeps the spherical metadata intact for proper playback, and provides an easy interface for refining immersive content.
With Filmora, you can import footage from a 360 camera or even start with 360-degree stock video, then enhance it with titles, music, or effects. The software also makes exporting for YouTube, Facebook, and VR headsets simple, ensuring your audience experiences the video as intended.

Step-by-Step Tutorial
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between 360 video and VR video?
360 video captures real-world environments using omnidirectional cameras, allowing viewers to look around in all directions but not move within the scene. VR (Virtual Reality) video is typically computer-generated and may allow for movement within the virtual environment (6 degrees of freedom), providing a more immersive experience. -
Do I need a special camera to shoot 360 video?
Yes, you need an omnidirectional camera or a multi-camera rig that can capture all directions simultaneously. Popular consumer options include Insta360, GoPro MAX, and Ricoh Theta series cameras. -
Can I watch 360 videos without a VR headset?
Yes, you can watch 360 videos on smartphones, tablets, and computers by dragging the screen to change the viewing angle. However, for a fully immersive experience, VR headsets are recommended. -
How much does it cost to produce 360 video content?
Costs vary widely depending on equipment, production quality, and editing needs. Consumer-grade 360 cameras start around $300-400, while professional setups can cost thousands. Editing can be done with affordable software like Filmora, but professional-grade editing may require more advanced tools. -
Which platforms support 360 video uploads?
Major platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and Vimeo support 360 video uploads. They can detect the 360 metadata and enable interactive viewing directly on their platforms without requiring special apps or plugins.




